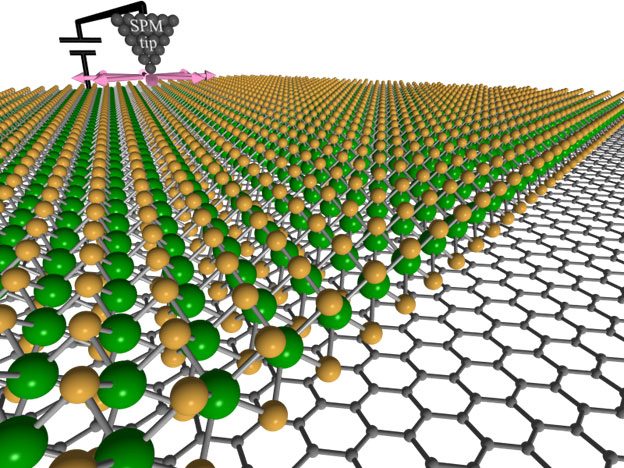
Advanced Computing Brings Autonomous Investigations to Nanostructured Surfaces
Machine learning and artificial intelligence accelerate nanomaterials investigations.

Machine learning and artificial intelligence accelerate nanomaterials investigations.
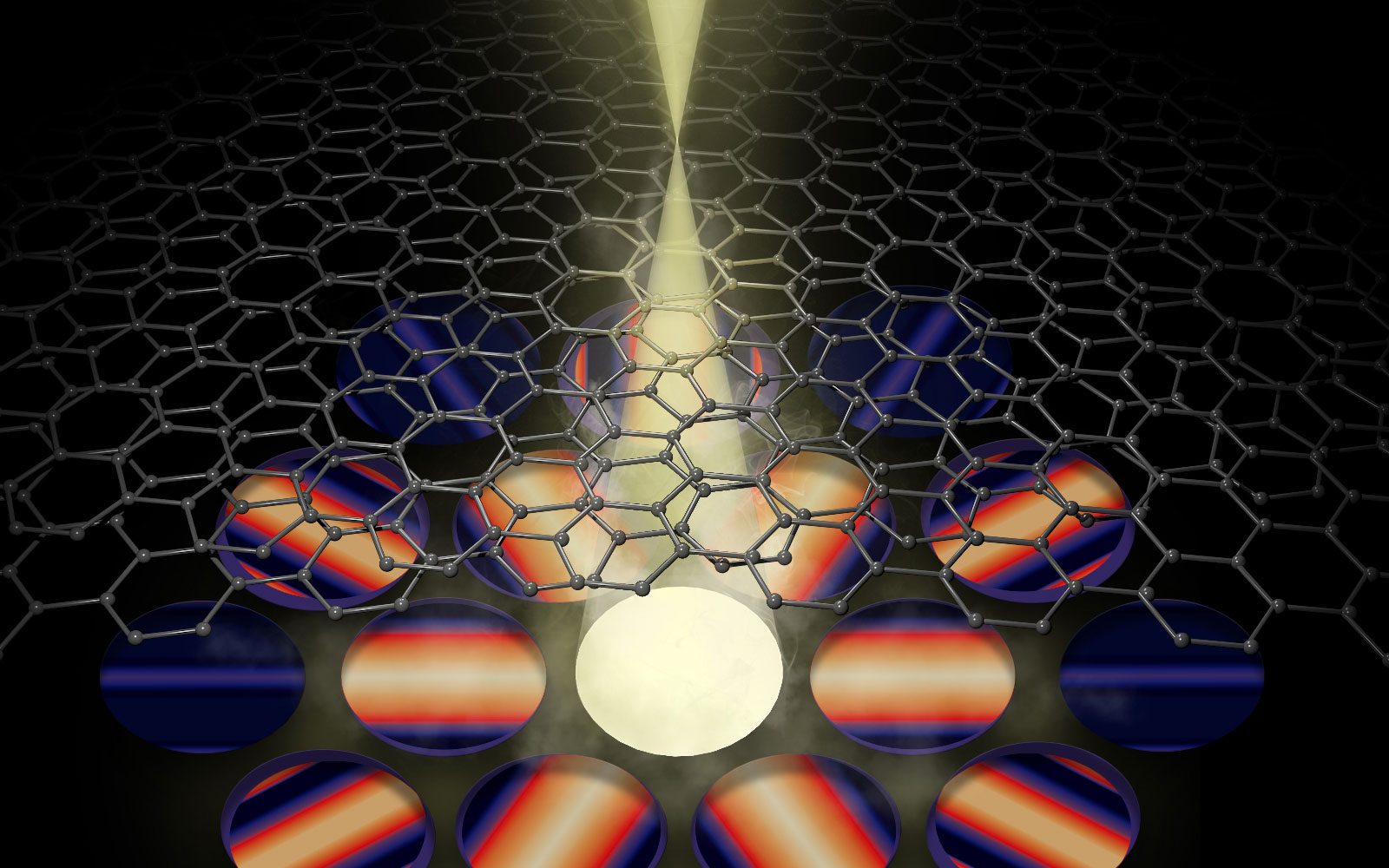
A new microscopy technique measures atomic-level distortions, twist angles, and interlayer spacing in graphene.
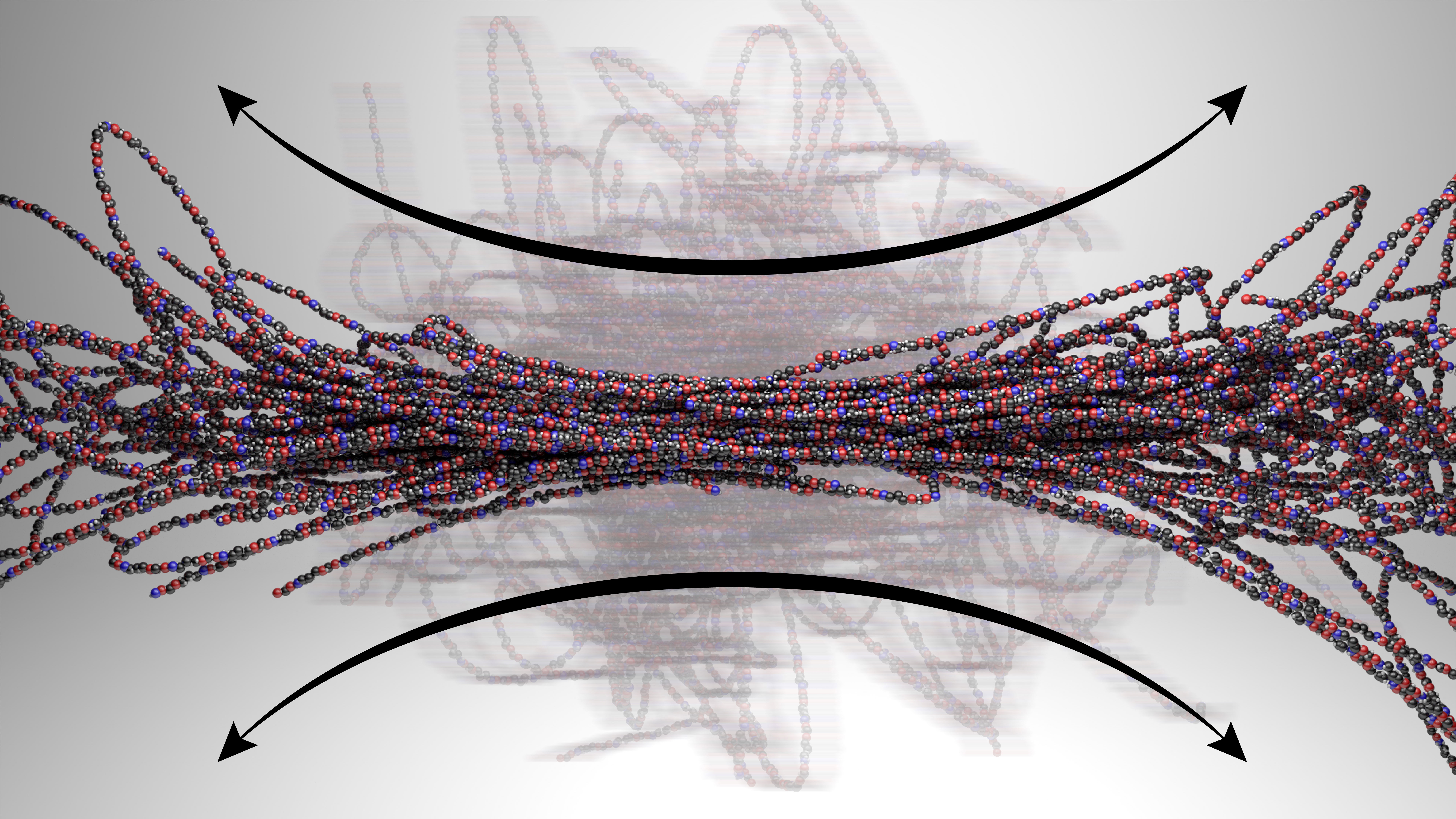
New computational methods “fingerprint” polymer motions under flow.
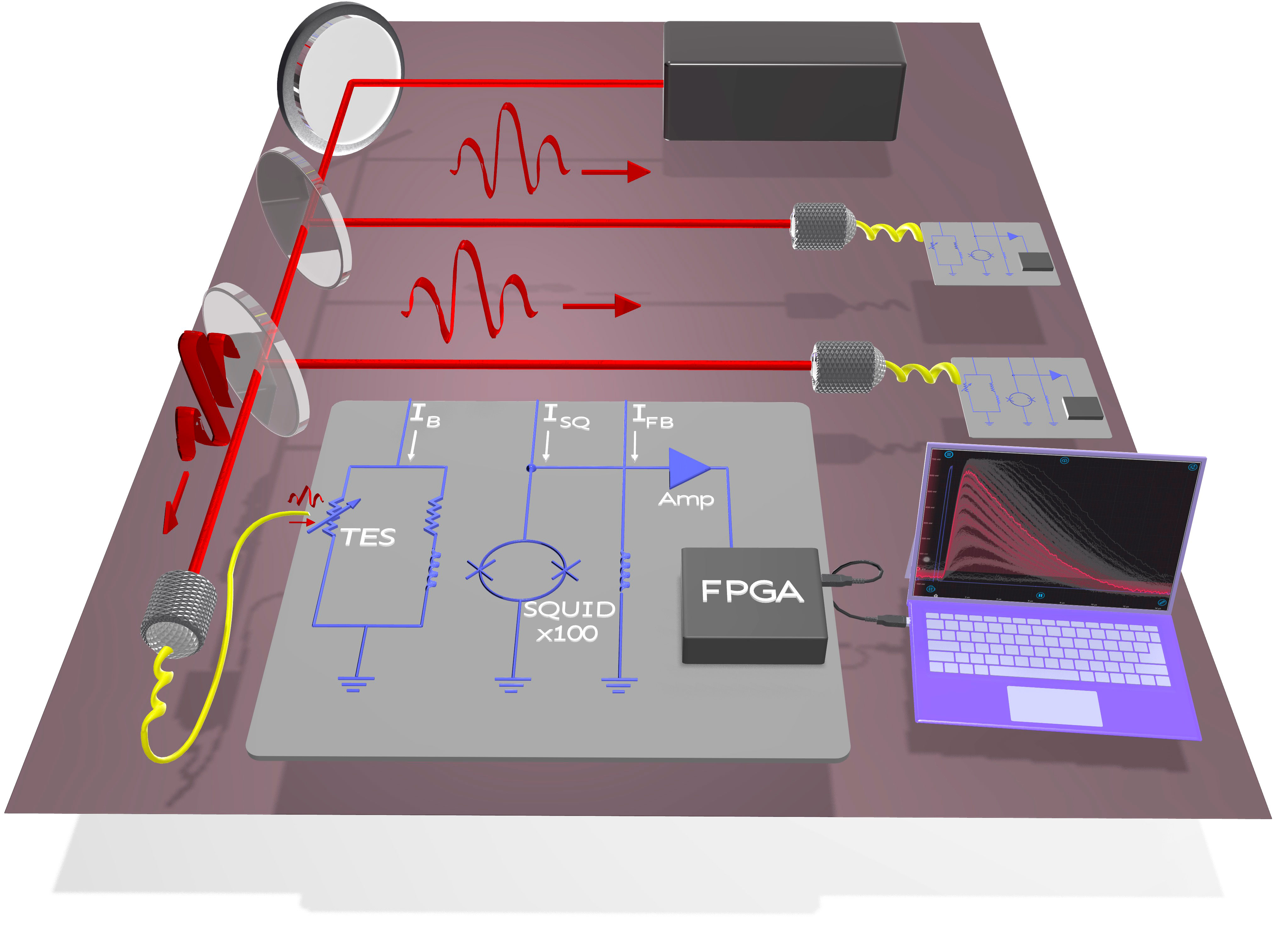
A new system for detecting photons in laser-powered quantum computers brings these systems closer to reality.
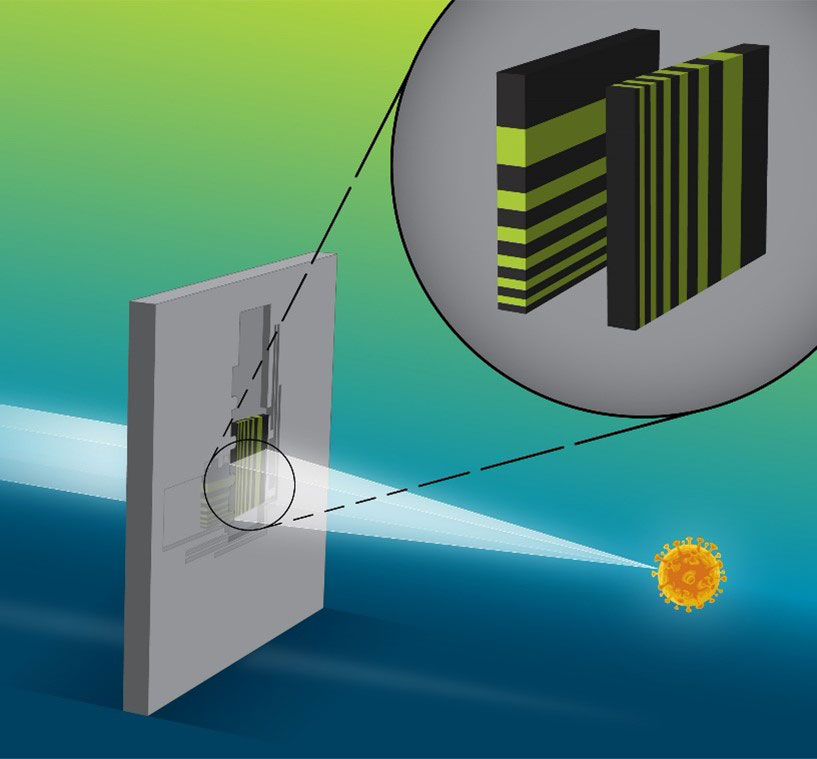
This new Laue lens system received a 2022 Microscopy Today Innovation Award.
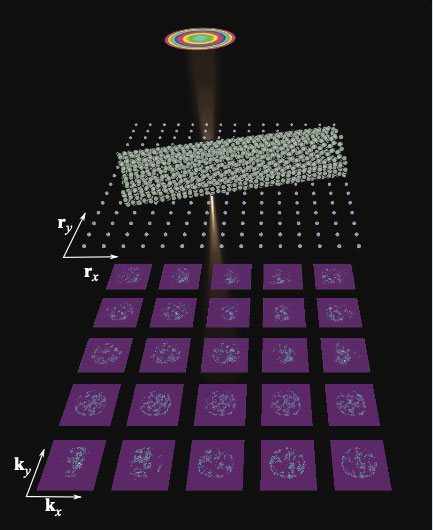
New algorithms allow real-time interactive data processing at 10X previous rates for electron microscopy data.
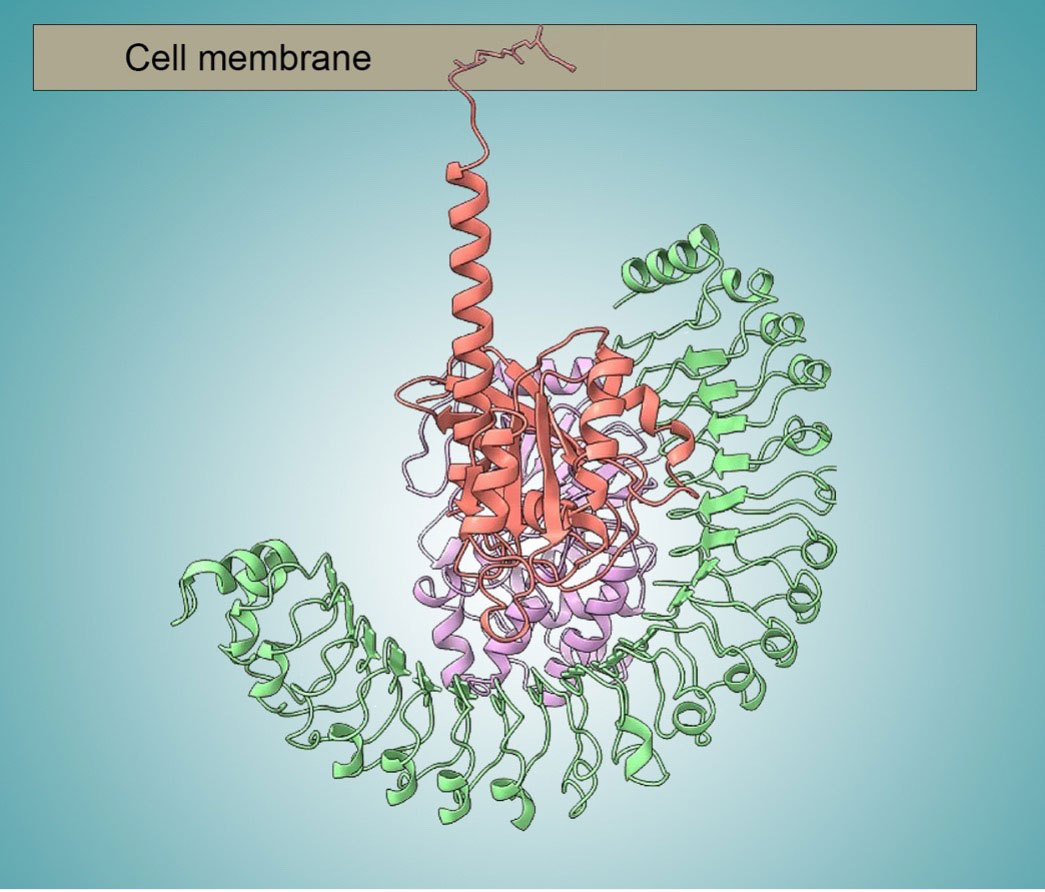
Three proteins work together to transmit signals for cell division, revealing new targets for cancer-fighting drugs.
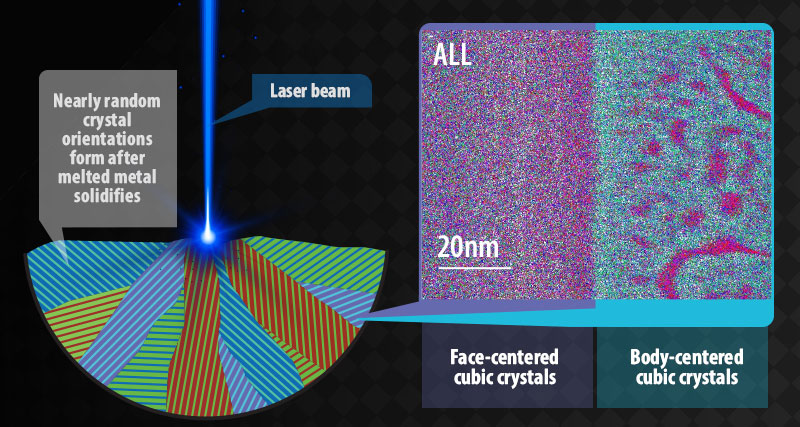
Laser-based additive manufacturing produces high-entropy alloys that are stronger and less likely to fracture.
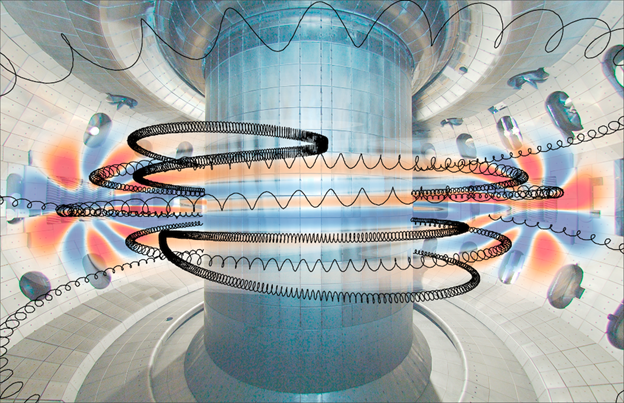
Computation and simulations show that different types of collisions compete to determine the way energy is transferred between particles and plasma waves.
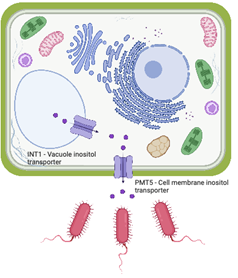
Scientists discover a mechanism for plant-microbe interactions.
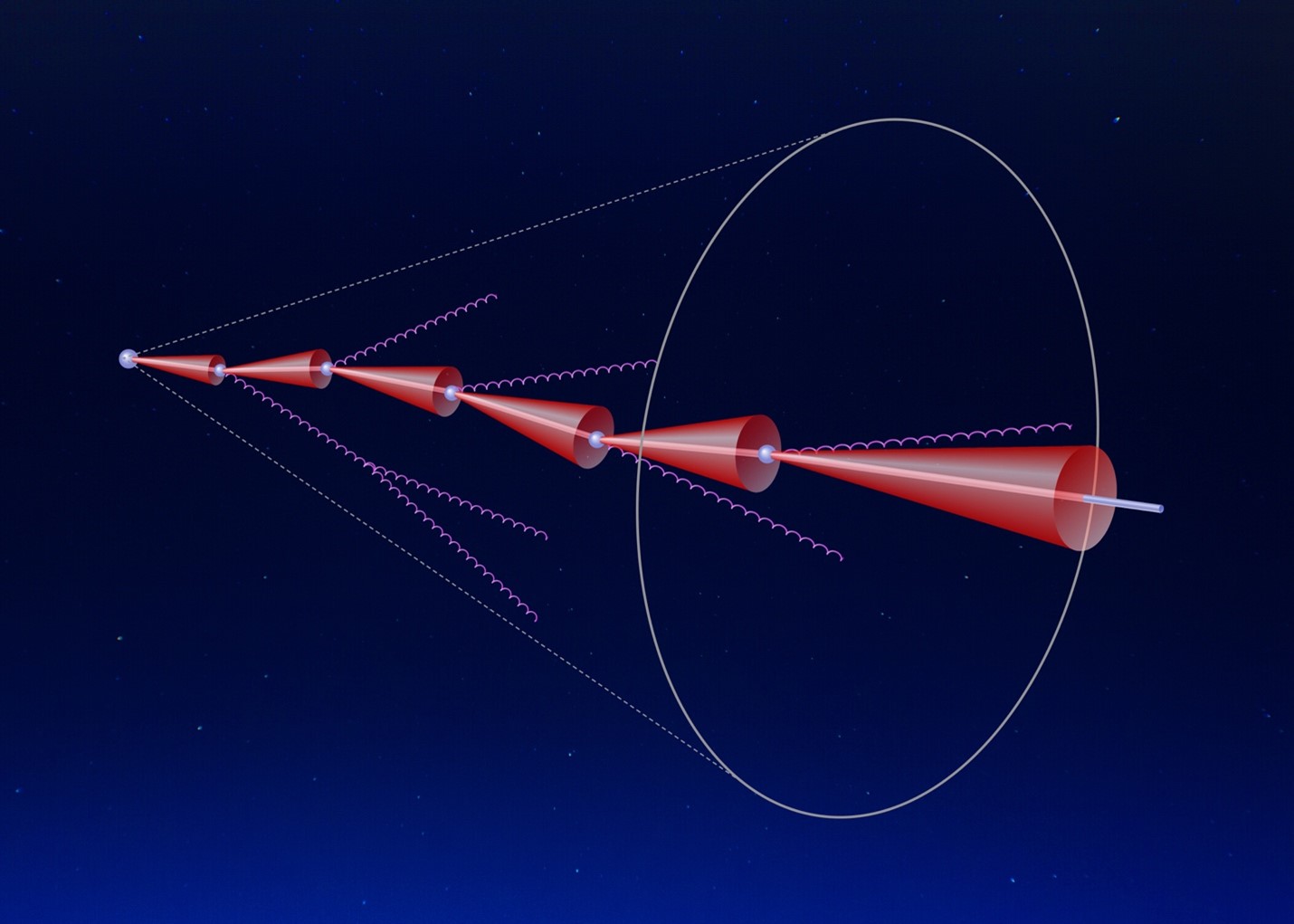
Novel techniques allow the first direct observation of a predicted effect that results in the suppression of gluon radiation emitted by a heavy quark.
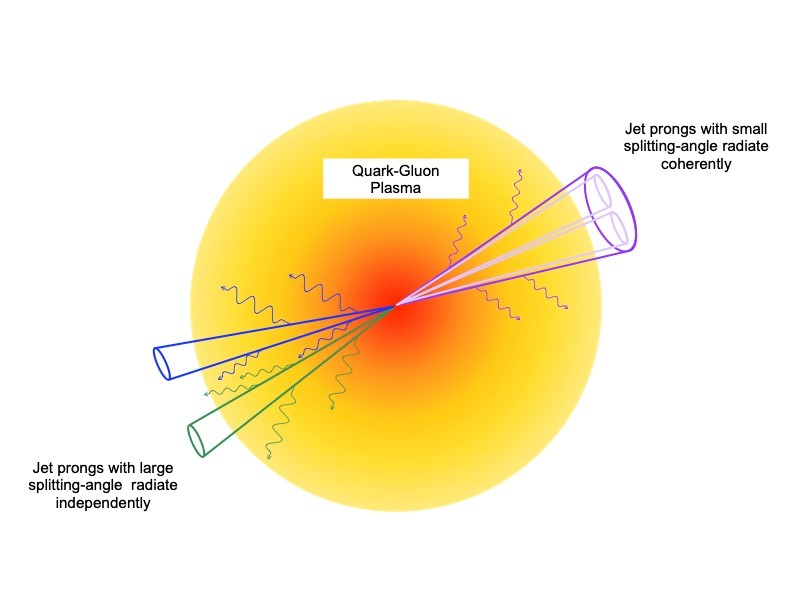
Jets of particles in quark-gluon plasma from heavy-ion collisions lose energy via radiation, but how they radiate energy depends on the jet’s structure.