
Protecting Against Large Damaging Energy Bursts in Fusion Energy Devices
Scientists found a potential way to suppress large damaging edge-localized modes, providing an approach to protect future devices.

Scientists found a potential way to suppress large damaging edge-localized modes, providing an approach to protect future devices.

Researchers identify butylamine as a promising solution to many challenges at biorefineries.

Researchers demonstrated an efficient strain of bacteria for bioproduction that grows on the promising feedstock formate.

Researchers have used an undulator’s magnetic field to generate and control ultrafast X-ray pulses.

Using the Advanced Light Source and Molecular Foundry, researchers identified the chemical stew found in samples of the asteroid Bennu.

The Uncertainty Toolbox, a popular open-source library for uncertainty quantification and calibration, is a valuable tool for fusion and other research.

Researchers gain a new understanding of the binding chemistry of radioactive antimony, opening doors for targeted therapy.

Using DNA scaffolding, scientists developed a universal method for producing a wide variety of functional, 3D metallic and semiconductor nanostructures
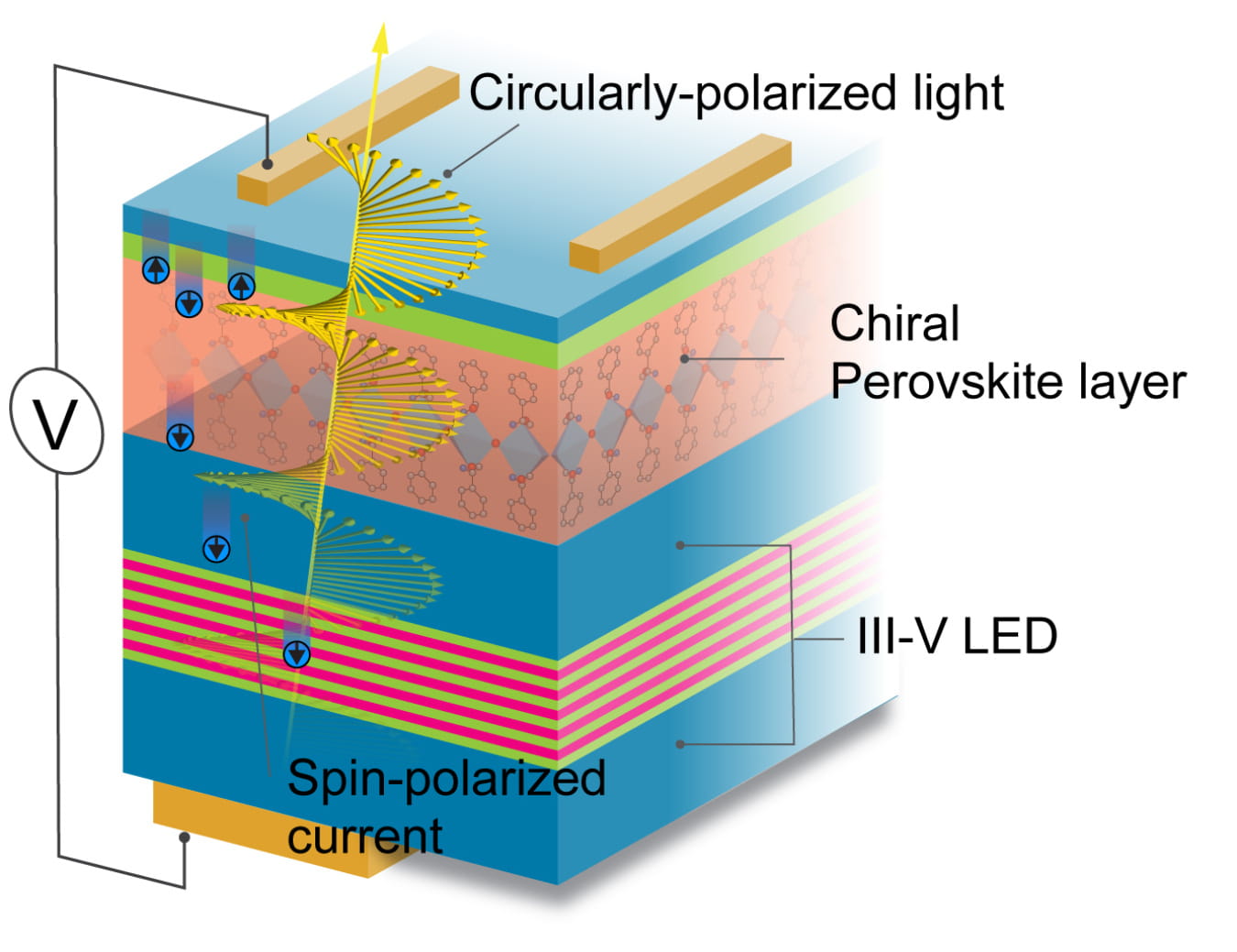
By combining a chiral semiconductor with an LED, scientists controlled the orientation of electron spin.
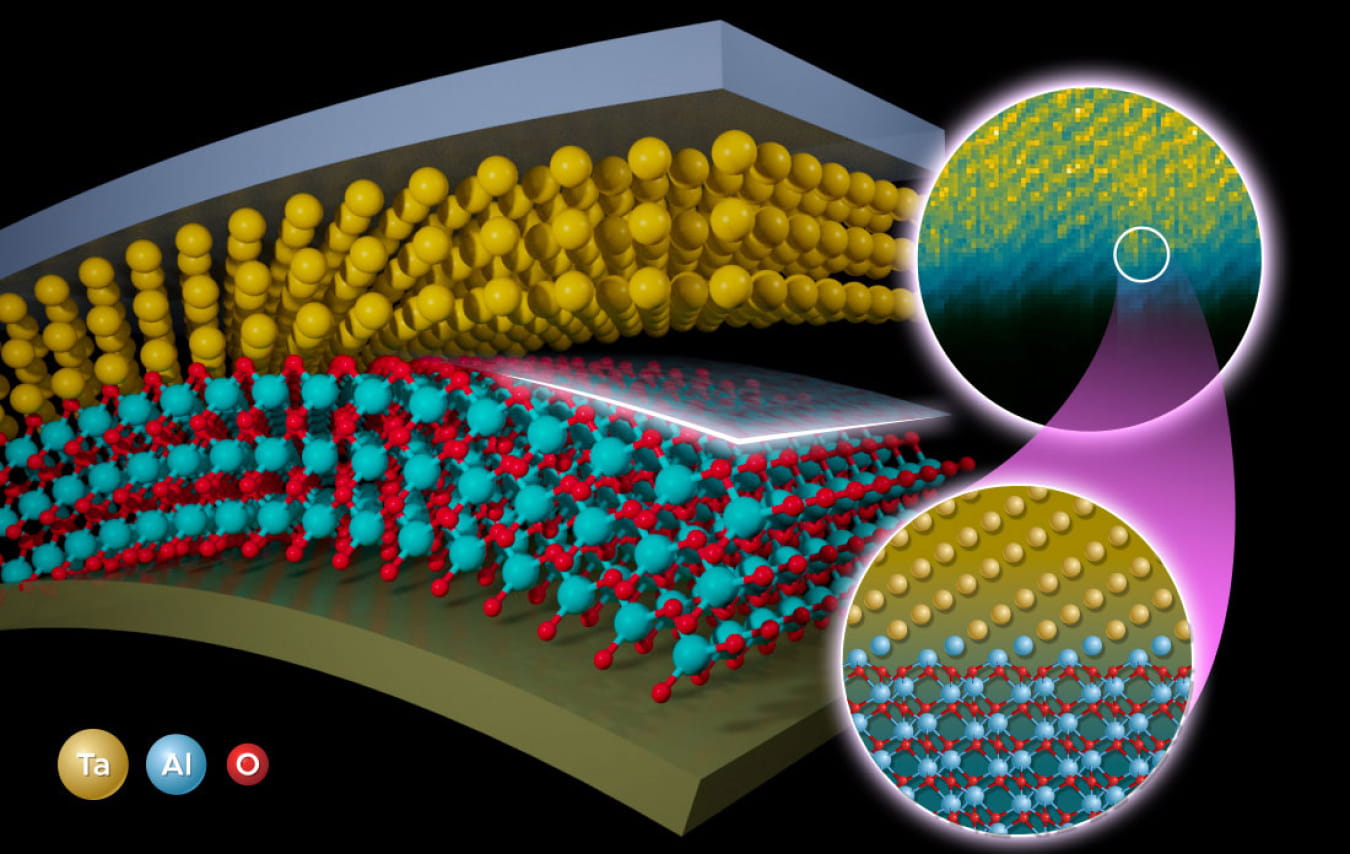
Researchers used a multimodal approach to determine the metal-substrate interface in a superconducting qubit material.

A new framework employs usage patterns to improve data placement.

Discovery proves the existence of the mysterious Wigner crystal — an unusual kind of matter made entirely of electrons.