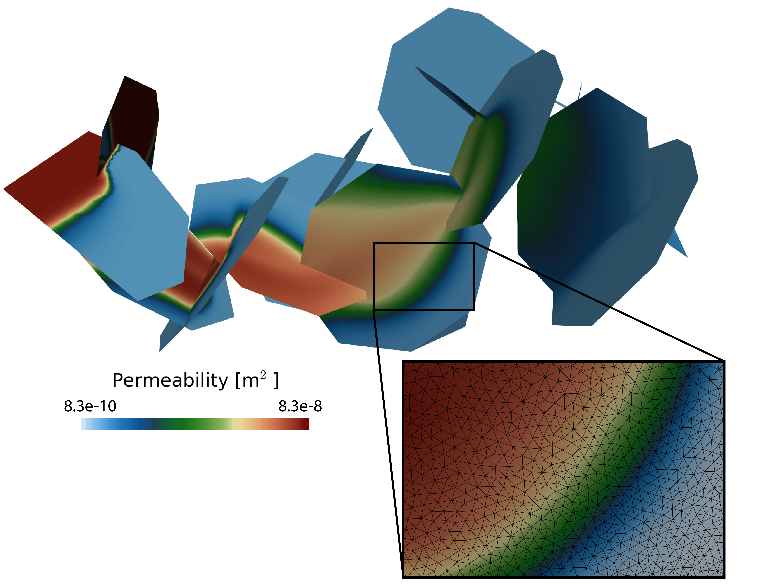
Filling in the Cracks: Scientists Improve Predictions for the Dissolution of Minerals in Rock Fractures
A new correction factor for predicting dissolution rates uses measurable geological properties in fractured media.

A new correction factor for predicting dissolution rates uses measurable geological properties in fractured media.
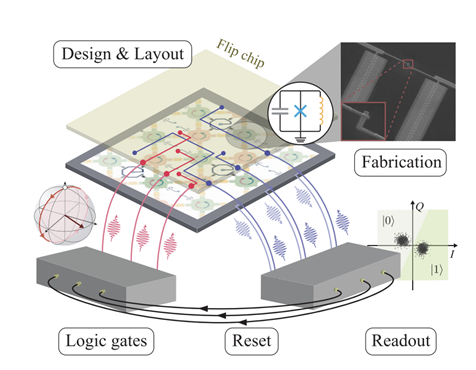
Fluxonium qubits can build cutting-edge quantum devices that will harness the potential of quantum computing.
Yarrowia lipolytica reallocates its production of protein toward energy and lipid metabolism to grow on hydrocarbons and produce high-value chemicals.

Microorganisms and their metabolisms help silica to mineralize near deep ocean methane seeps.
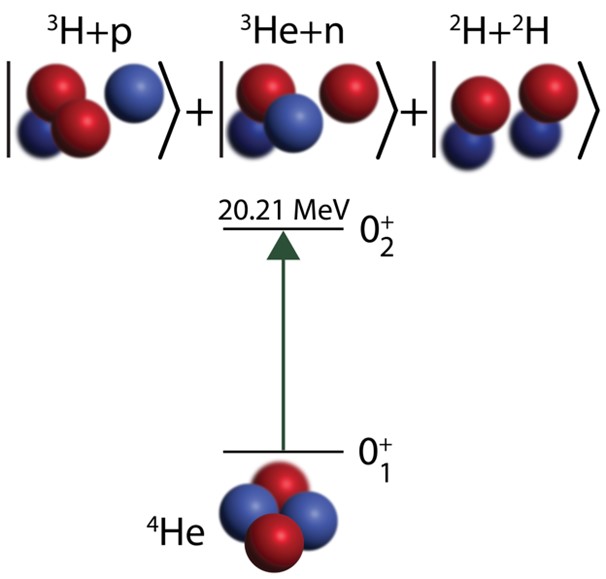
A new experimental measure of Helium-4’s transition from its ground energy state to an excited state closes an apparent gap with theoretical predictions.
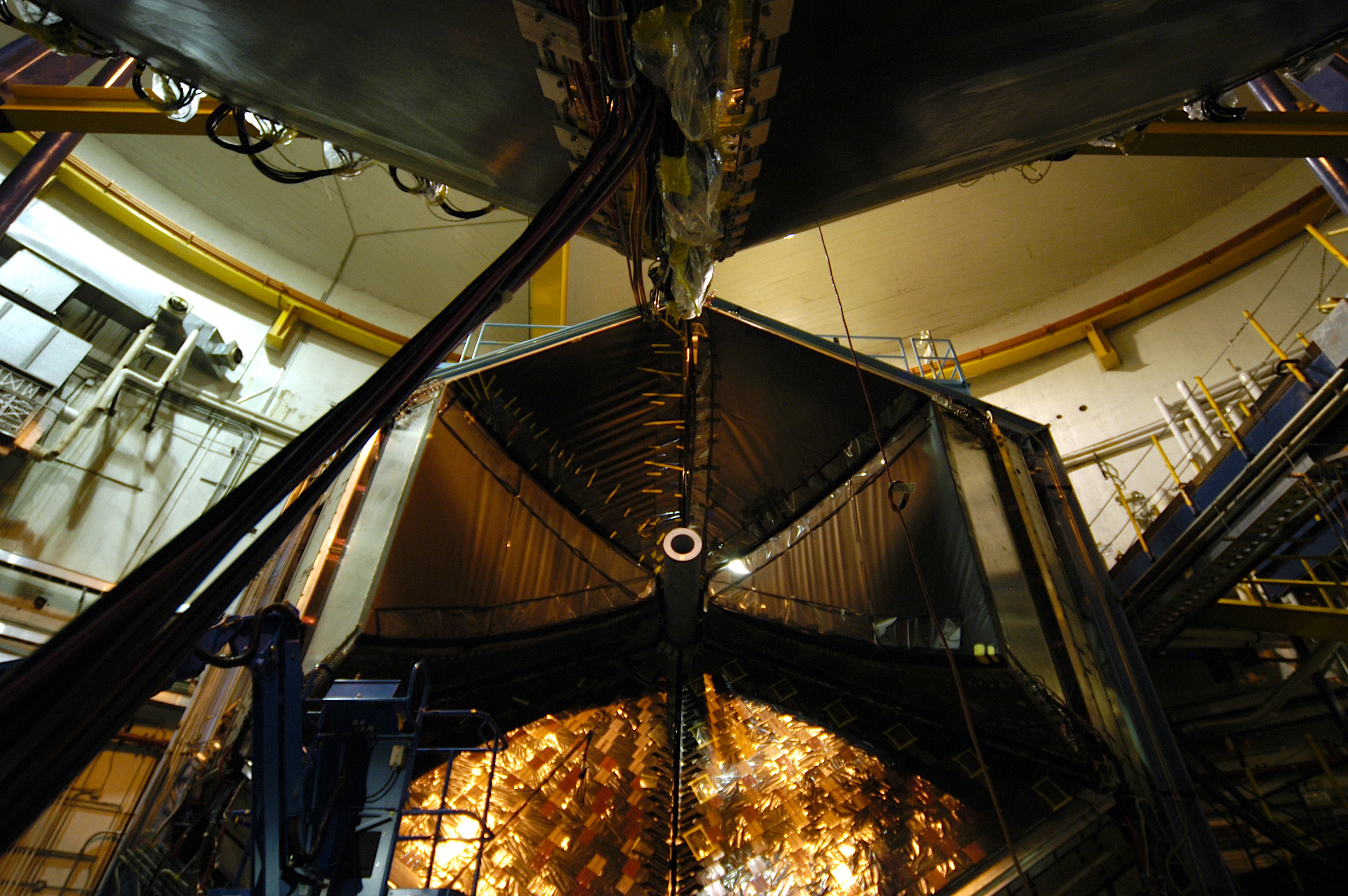

New insights reveal details of how strange matter forms.
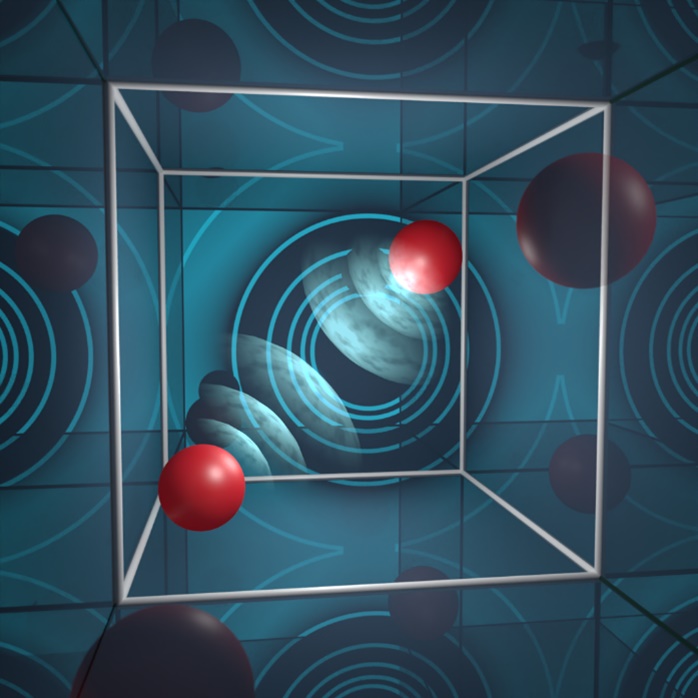
Finite geometry reveals fundamental properties of charged quantum systems.
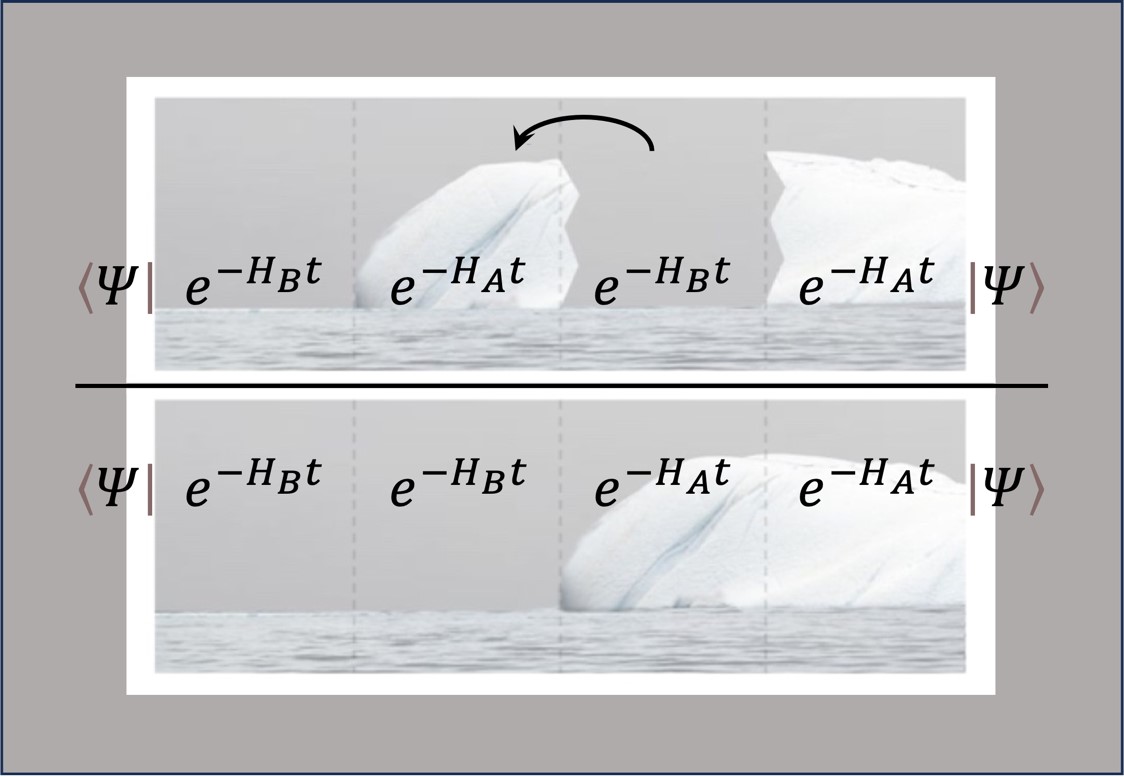
The floating block method provides the tools to compute how quantum states overlap and how to build fast and accurate emulators of those systems.
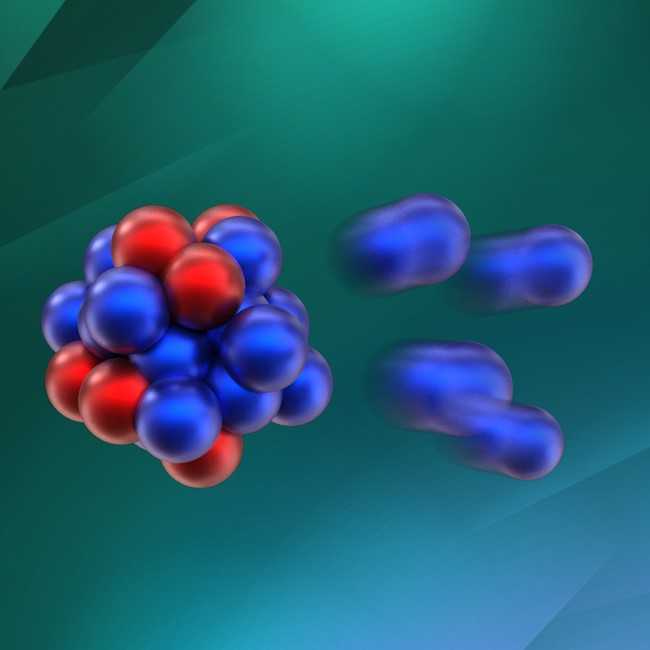
An almost-bound isotope of oxygen undergoes four-neutron decay that challenges theory.
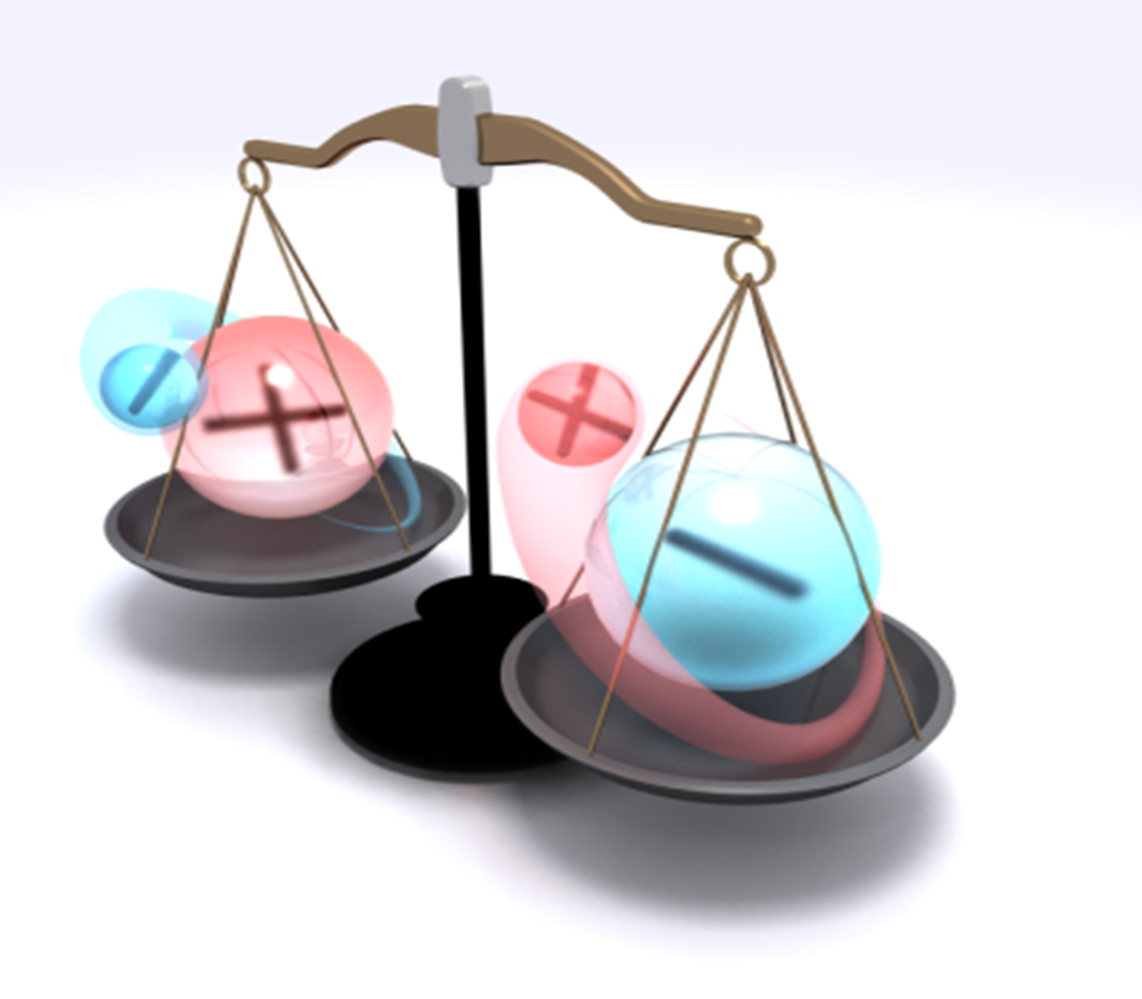

Settling a long-standing question, scientists have proven that antihydrogen falls downward in a first-ever direct experiment.

Experiments find increased temperatures and carbon dioxide rapidly altered peatland carbon stocks, highlighting peatlands’ vulnerability to climate change.
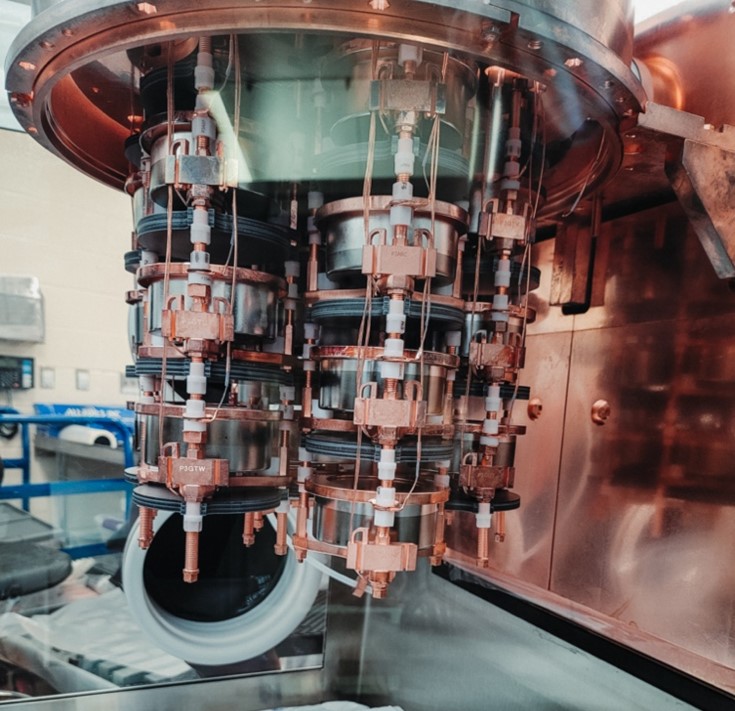

The first results from the MAJORANA experiment dramatically improve current limits on this rare isotope’s decay.