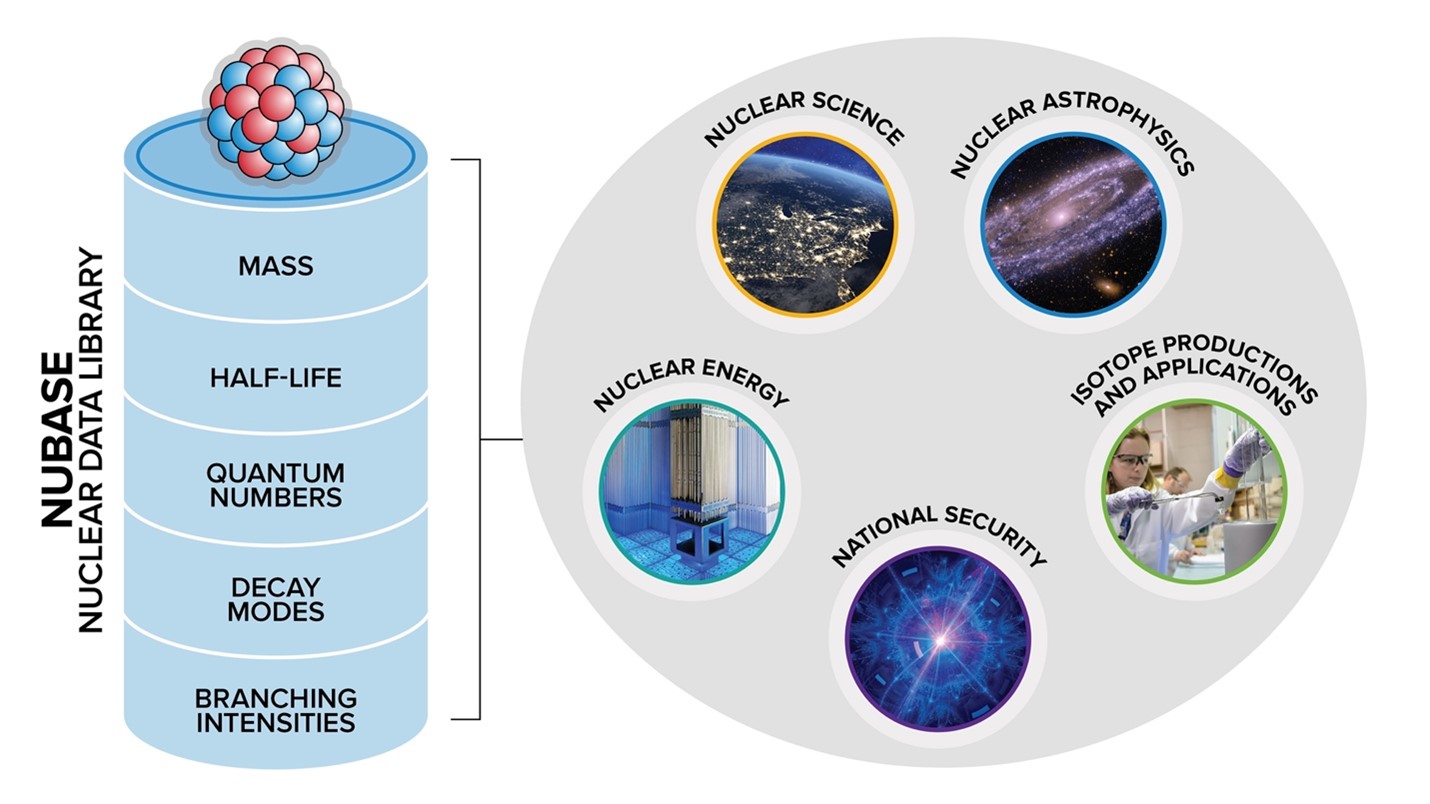
Database Supplies Recommended Key Properties for All Known Nuclei
Scientists in nuclear physics, astrophysics, energy, national security, and medicine use a source of recommended nuclear data to advance their research.

Scientists in nuclear physics, astrophysics, energy, national security, and medicine use a source of recommended nuclear data to advance their research.
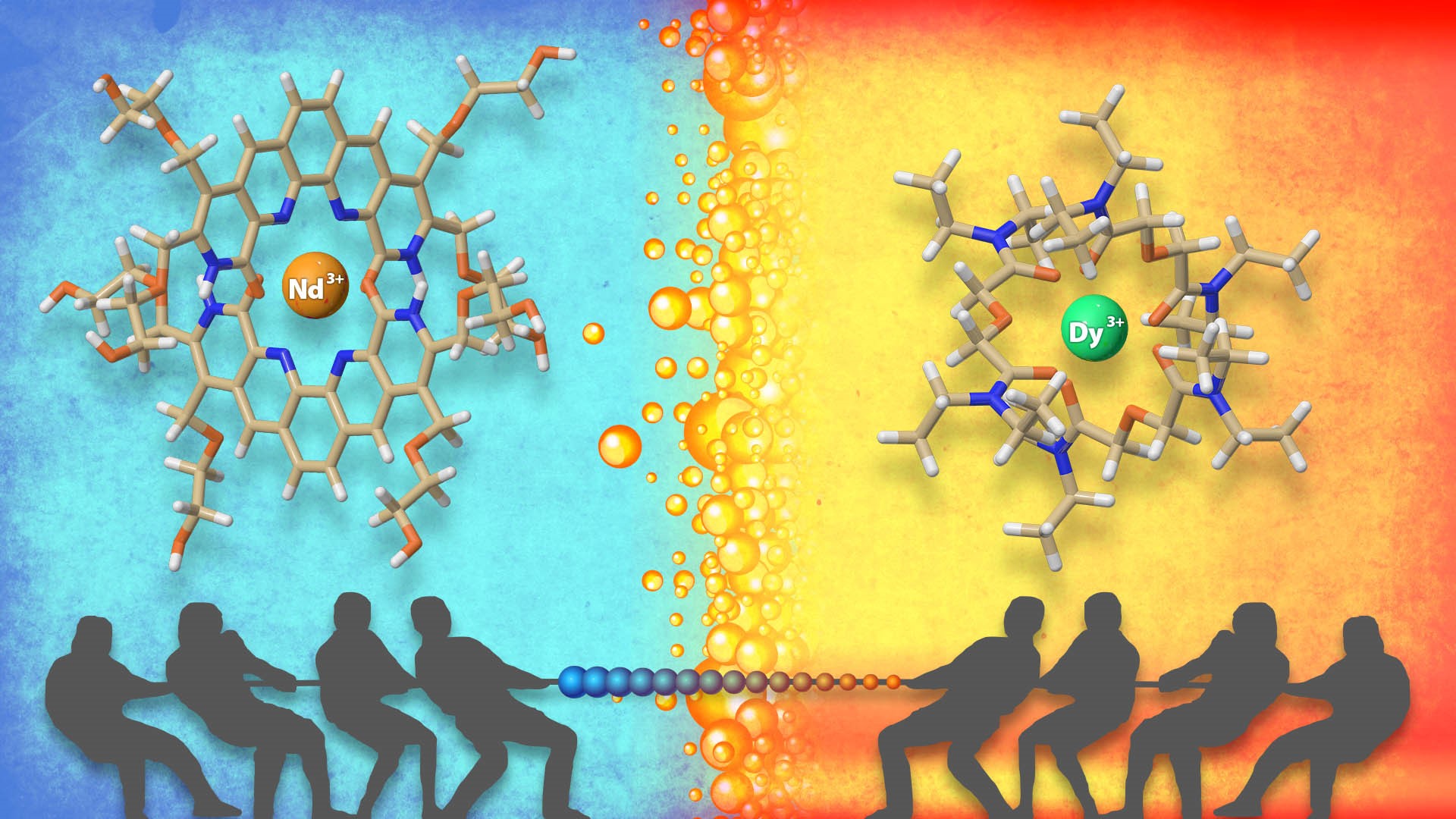
Opposing teams of water-loving and oil-loving molecules separate metals called lanthanides that are important in developing clean energy technologies.
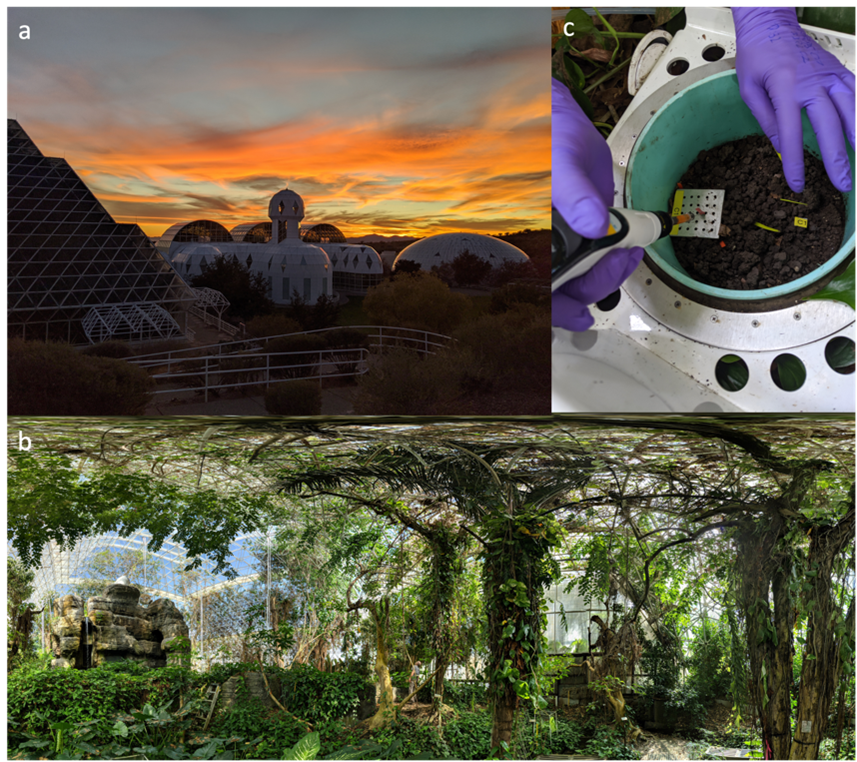

In a warmer world, microbes in drought-stricken soils convert less carbon to carbon dioxide and more to volatile intermediates.
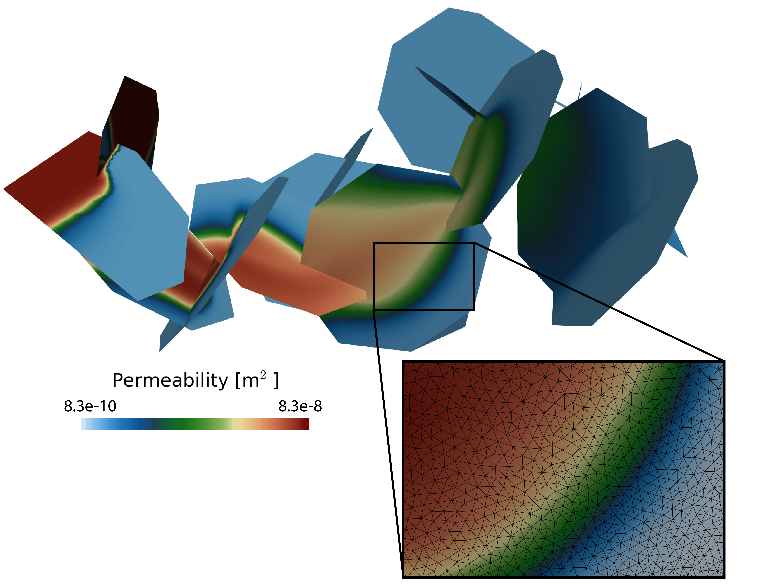
A new correction factor for predicting dissolution rates uses measurable geological properties in fractured media.
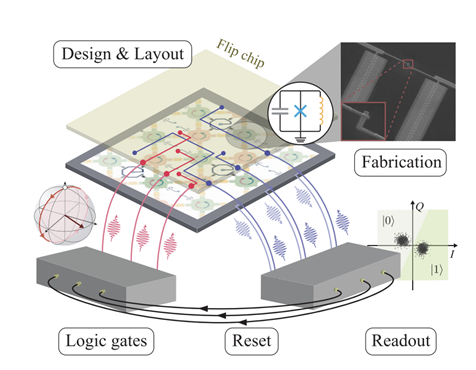
Fluxonium qubits can build cutting-edge quantum devices that will harness the potential of quantum computing.
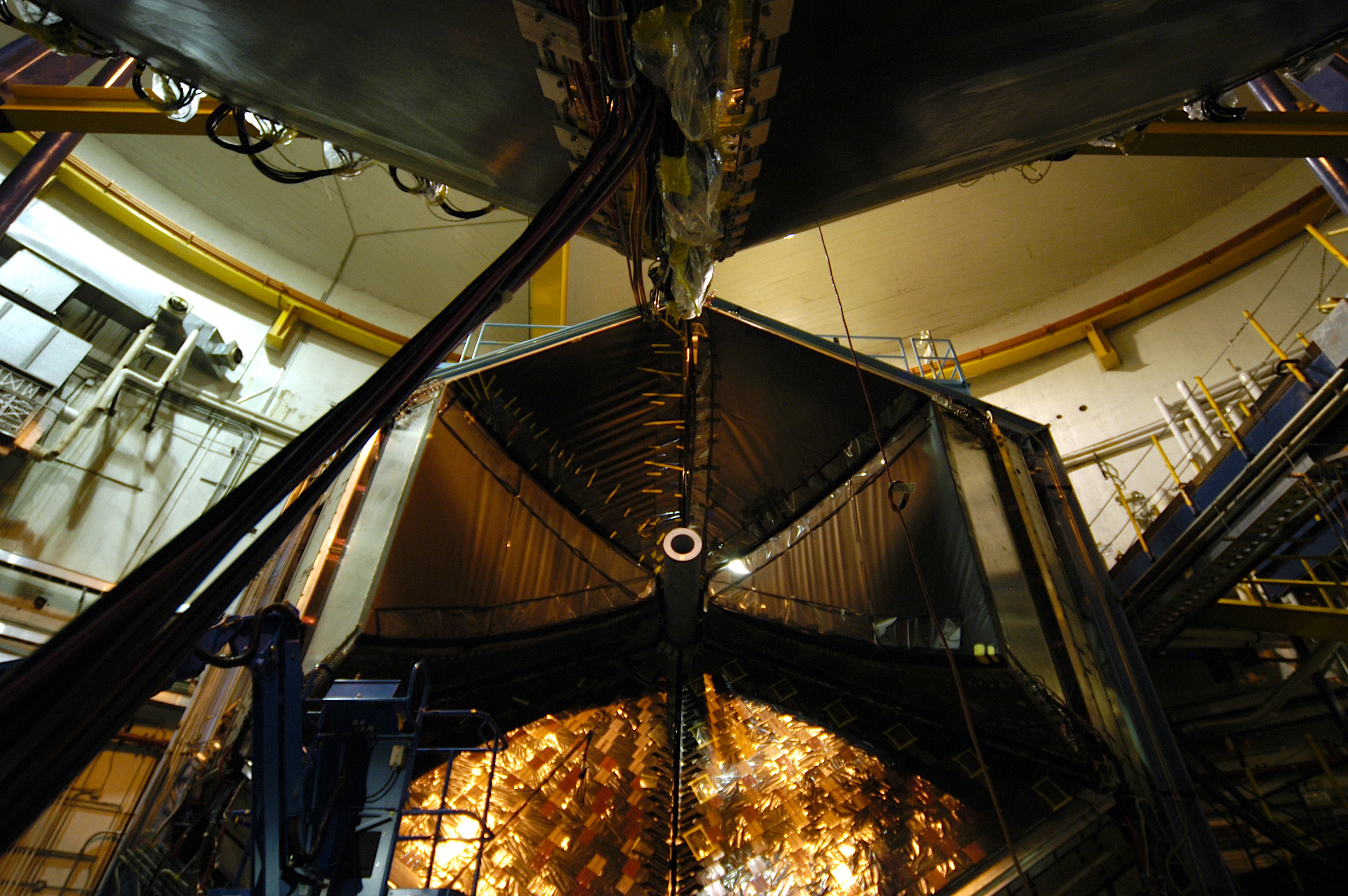

New insights reveal details of how strange matter forms.
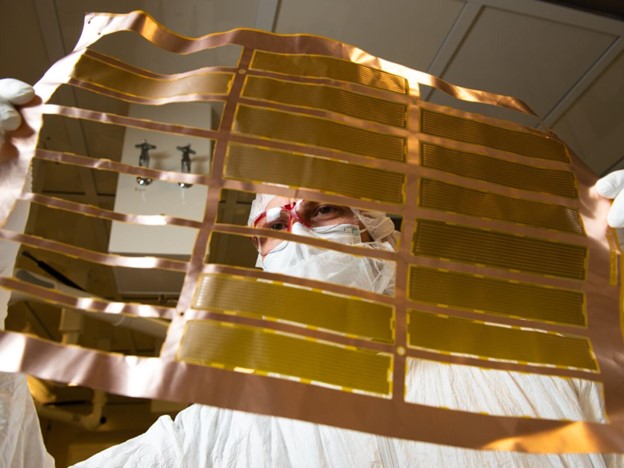

Researchers design ultra-low radiation cables to reduce background noise for highly sensitive nuclear decay and dark matter detectors.
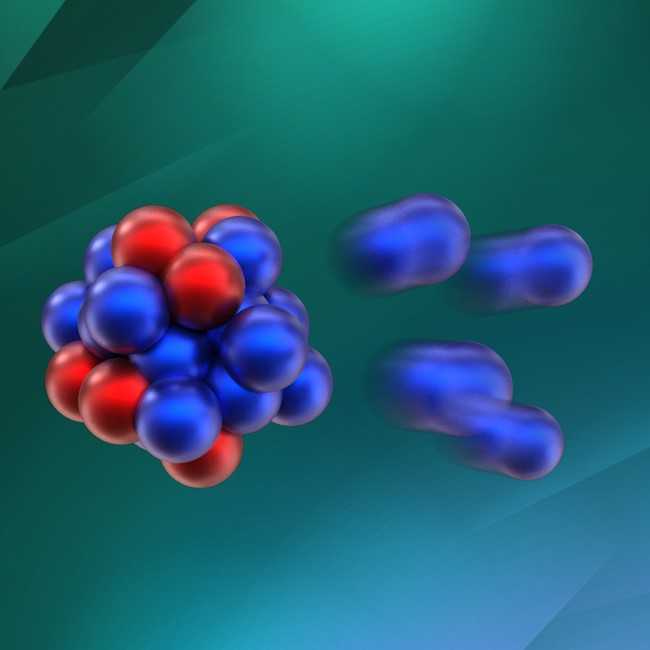
An almost-bound isotope of oxygen undergoes four-neutron decay that challenges theory.

Experiments find increased temperatures and carbon dioxide rapidly altered peatland carbon stocks, highlighting peatlands’ vulnerability to climate change.
![Composite of geopotential heights [m] (contours) and anomalies (colors) at 700 Hectopascal (hPa) of air pressure for each SOM node. These nodes help unpack how high- and low-pressure systems and other climate factors contribute to Texas rainstorms.](/-/media/ber/images/highlights/2024/High-Pressure-Systems.png?h=844&w=964&la=en&hash=810D3A676C1F7B8F0ABA215C5C39868B405F98E694DB597BB96940FE74D7CAE9)
AI reveals relationships between weather systems and cloud physics.
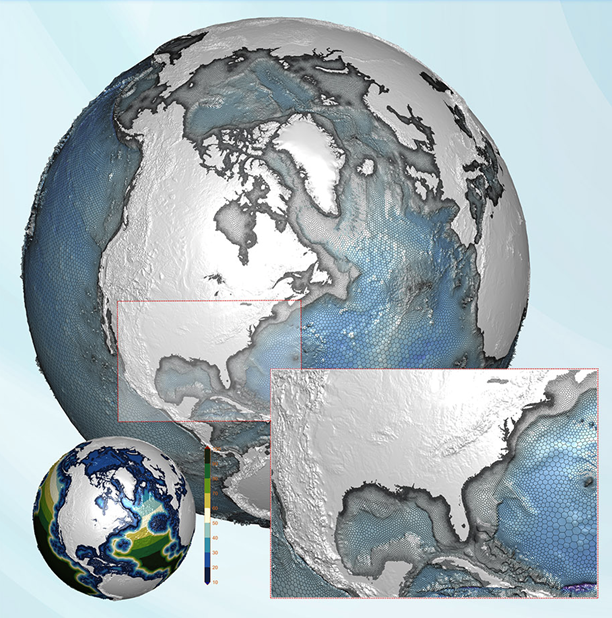
Voronoi tessellation meshes focus on sea ice areas of interest and reduce computer resource needs.
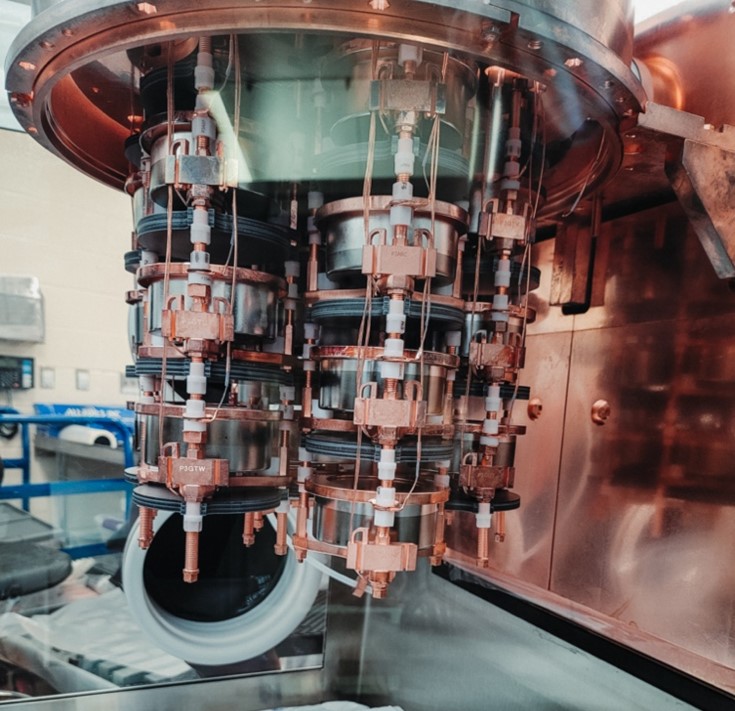

The first results from the MAJORANA experiment dramatically improve current limits on this rare isotope’s decay.