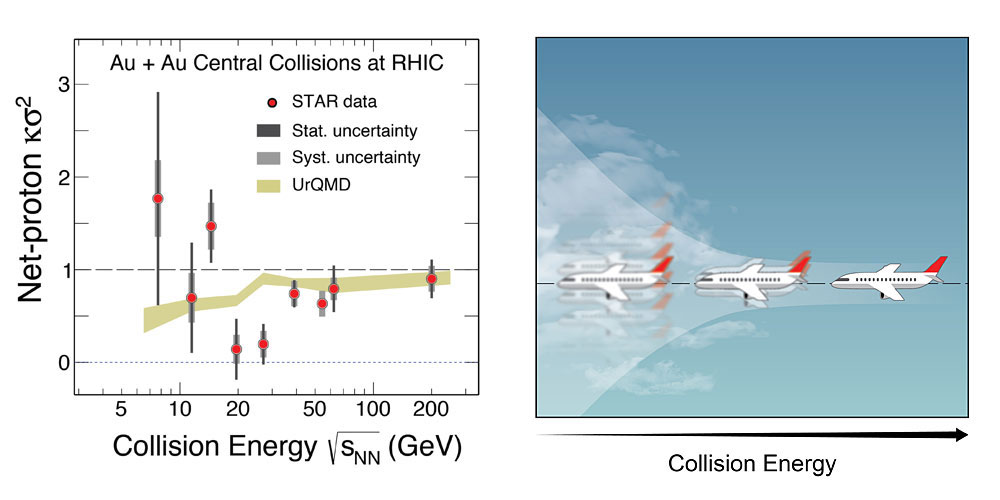
Signs of “Turbulence” in Collisions that Melt Gold Ions
Fluctuations in data from collisions of gold nuclei hint at a possible ‘critical point’ in how nuclei melt.

Fluctuations in data from collisions of gold nuclei hint at a possible ‘critical point’ in how nuclei melt.
The types of ancient stellar explosions that gave rise to meteoric presolar grains can now be identified thanks to observations of gamma rays emitted by the argon-34 isotope

Nuclear theorists put pen to paper and code to computer to detail this subatomic particle’s inner structure.

Scientists conduct the first direct probes of the interactions between protons and neutrons inside nuclei.
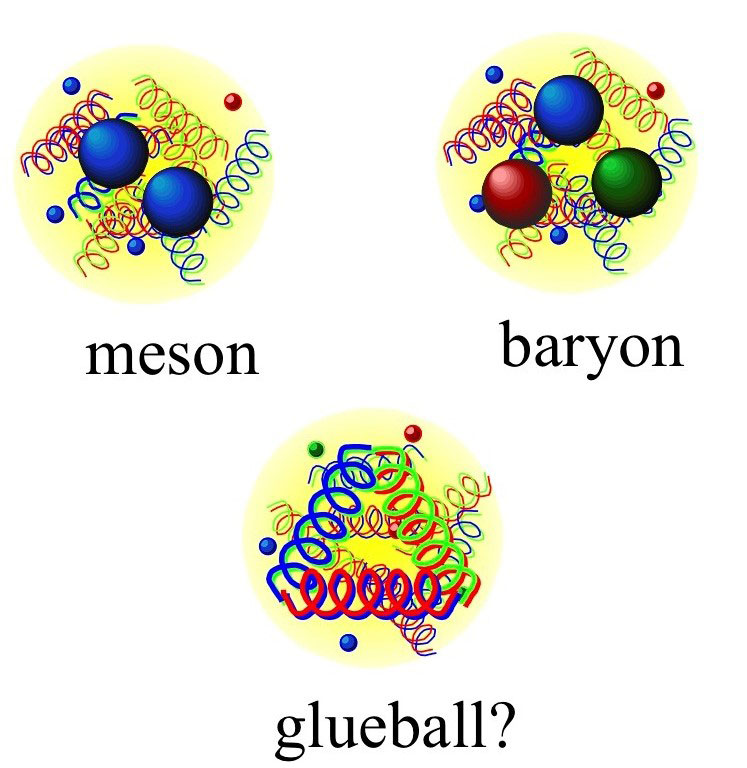
Scientists predict that gluons, the particles that bind quarks, also bind to one another, but they have never unambiguously observed globs of pure ‘glue.’
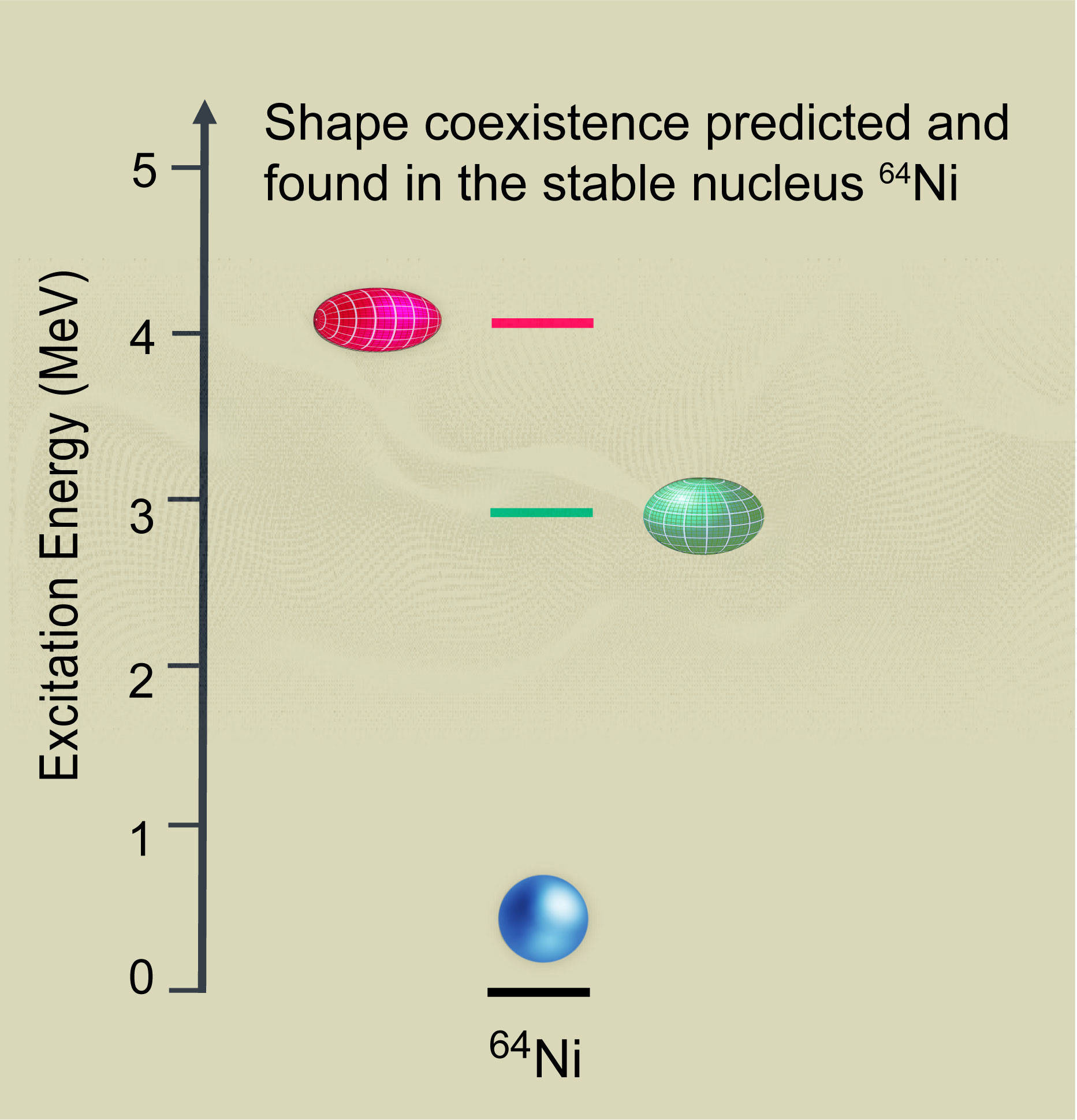
Scientists track down coexistence of multiple shapes in the Nickel-64 nucleus: a spherical ground state and elongated and flattened shapes.
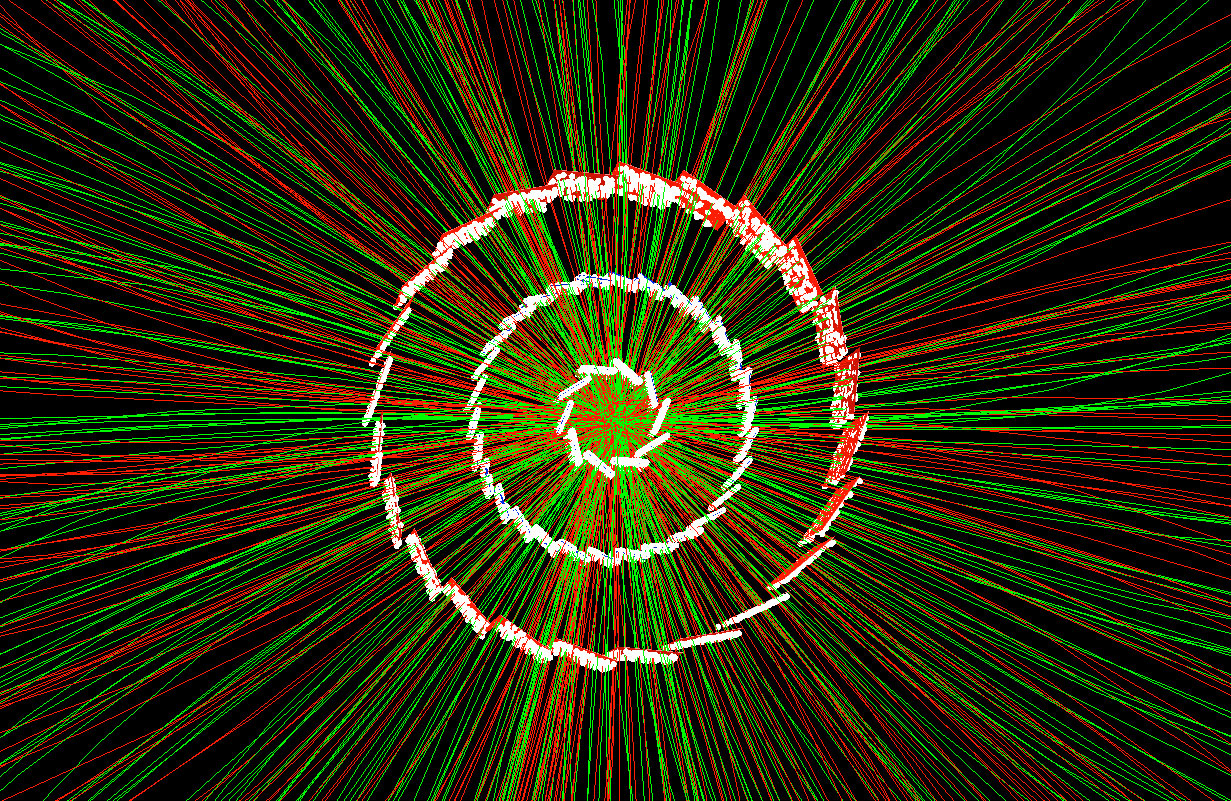

Tracking particles containing charm quarks offers insight into how quarks combine.
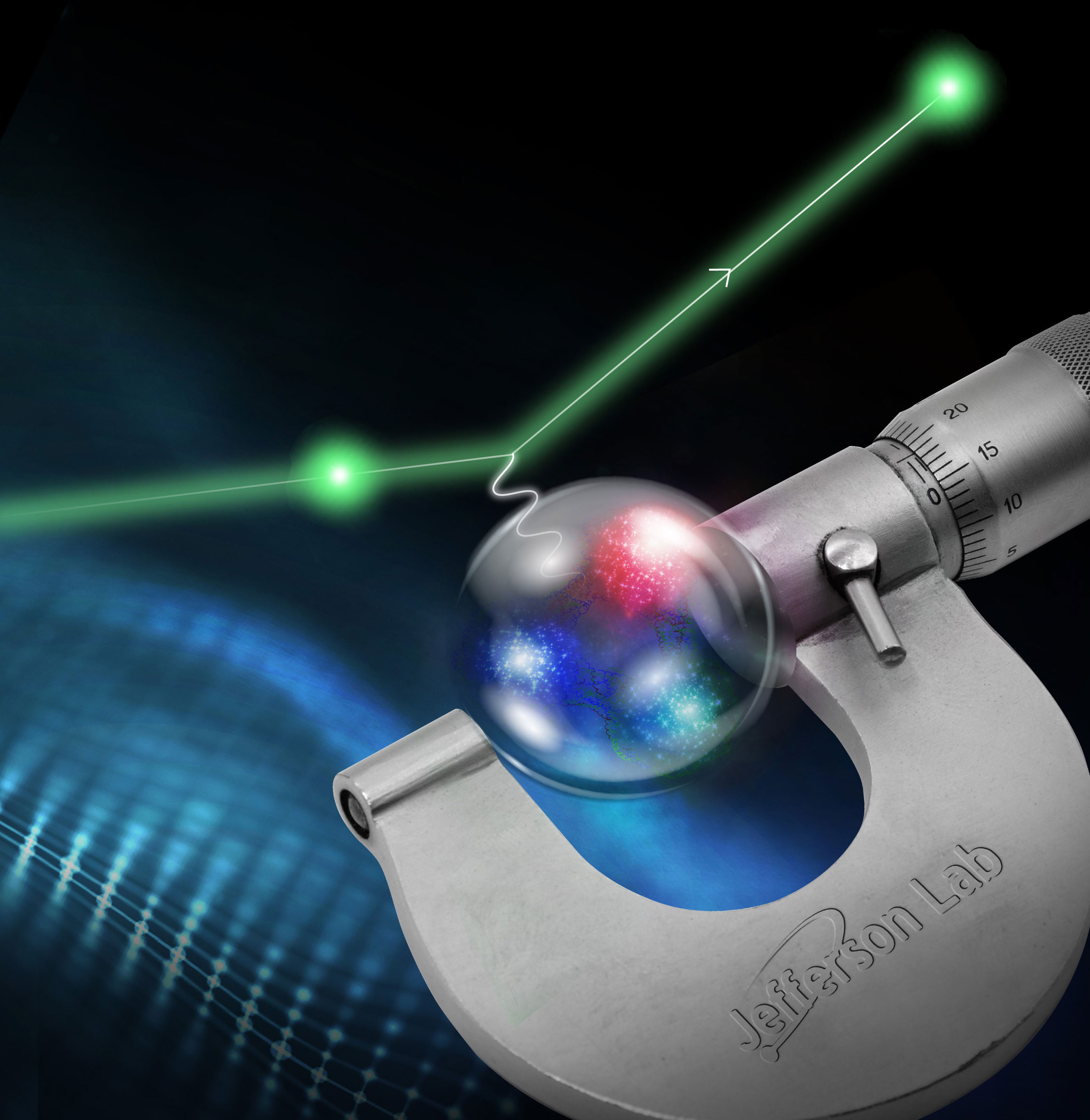

Physicists get closer to solving the proton radius puzzle with unique new measurement of the charge radius of the proton.

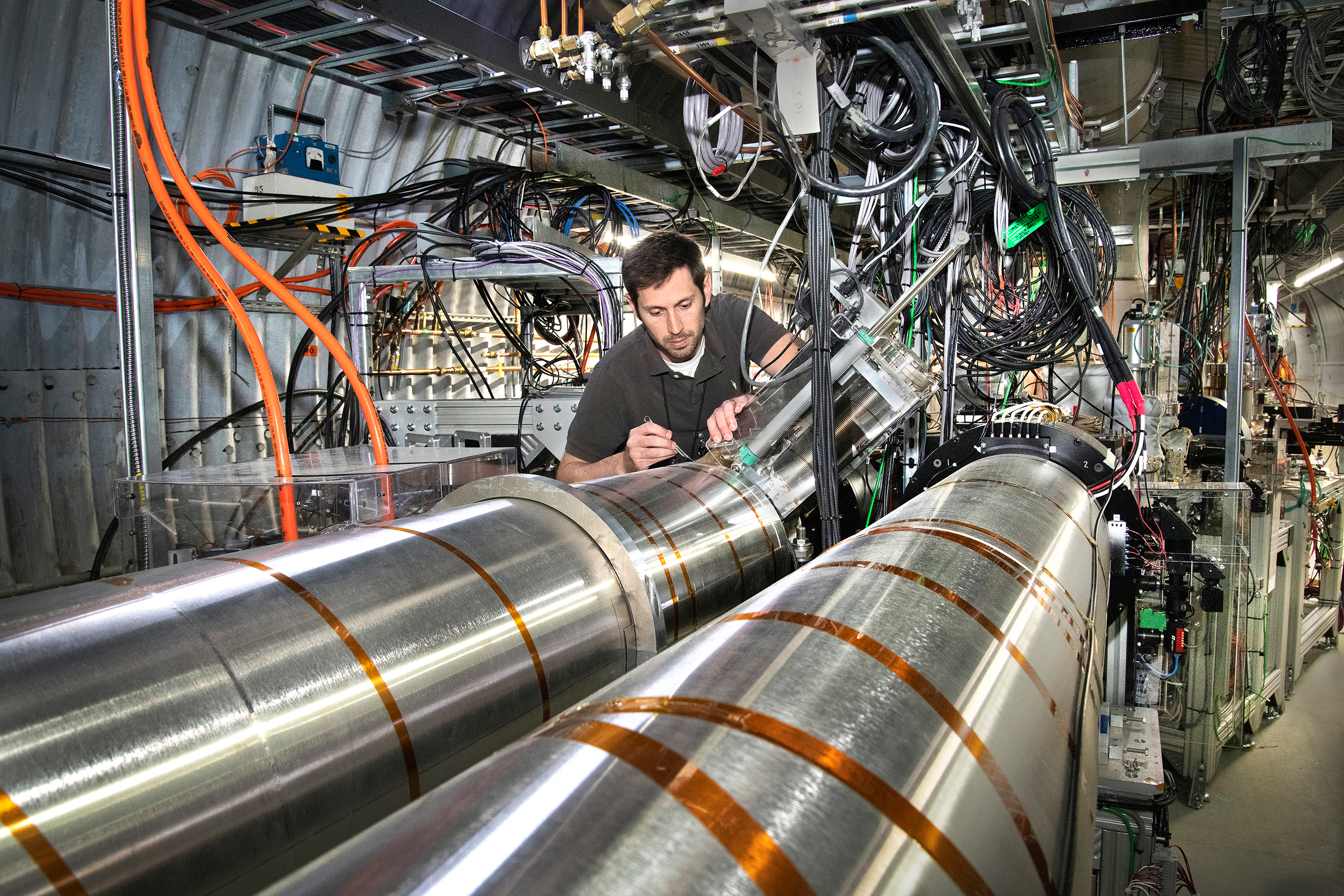
New measurements offer insights into binding interactions that glue fundamental building blocks of matter together.

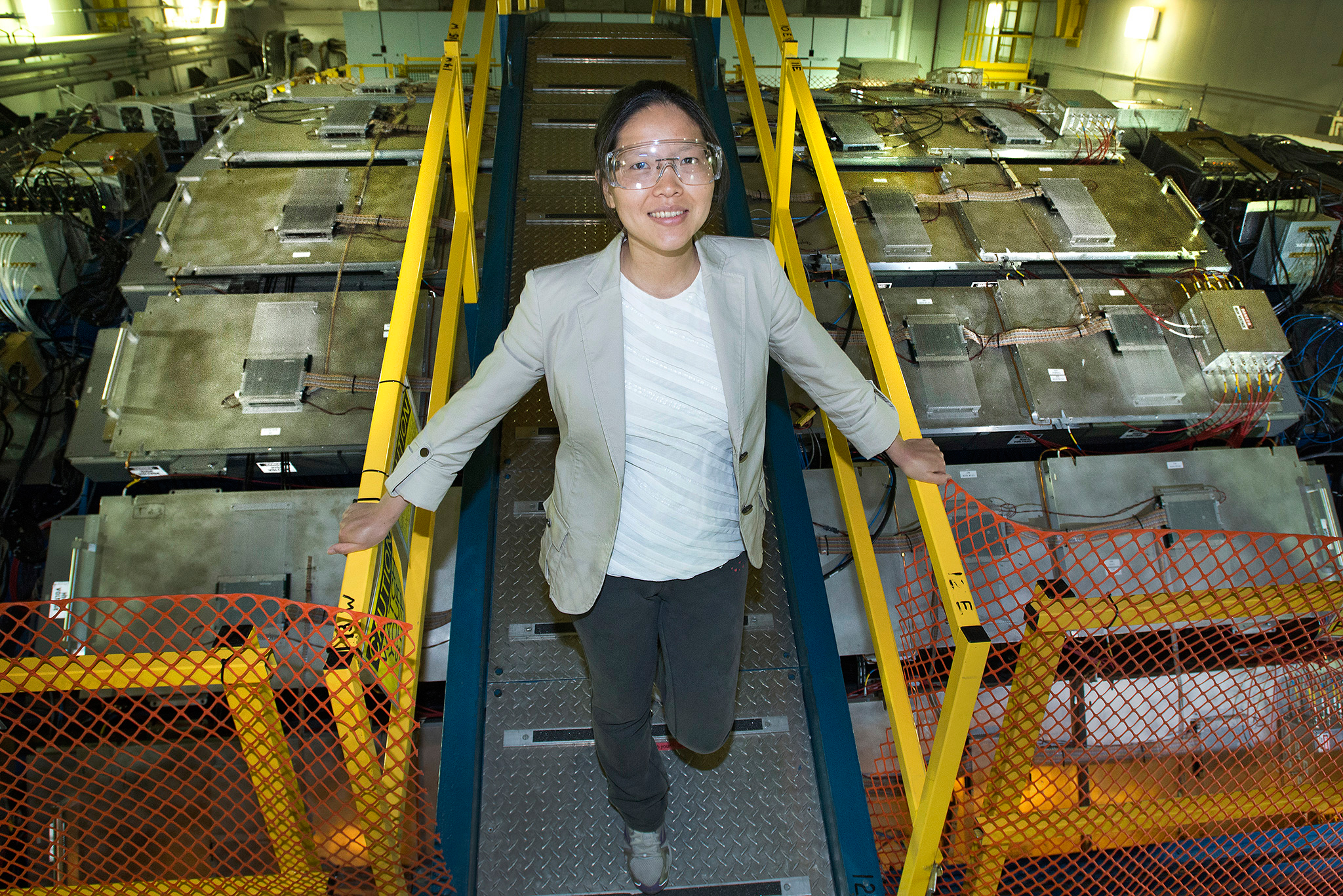
Team combines many innovative accelerator accomplishments to keep gold ions cold and advance nuclear physics research.
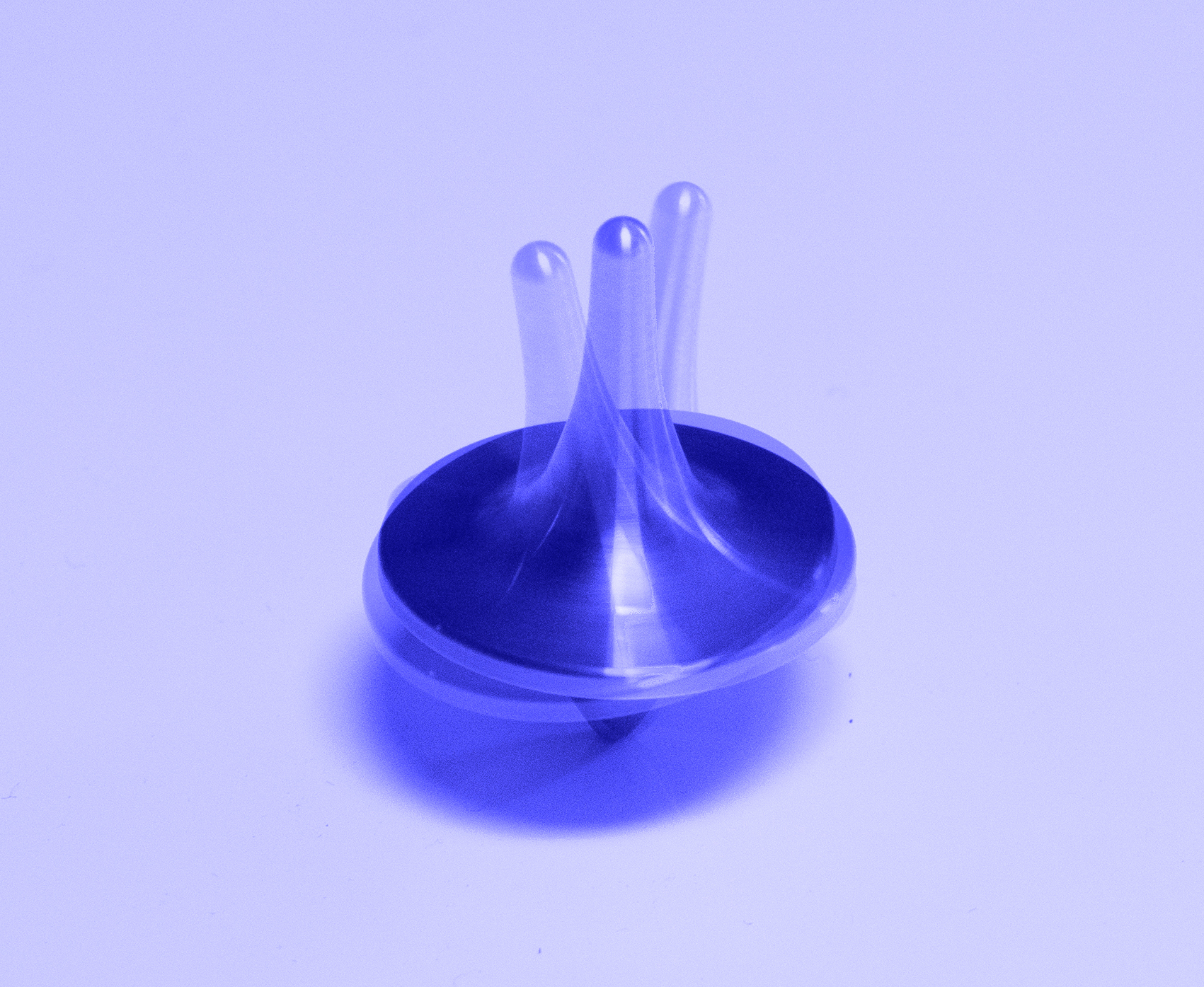

Diagnostic test will improve performance of collider as physicists explore sources of proton spin
Low-momentum (wimpy) quarks and gluons contribute to proton spin, offering insights into protons’ behavior in all visible matter.