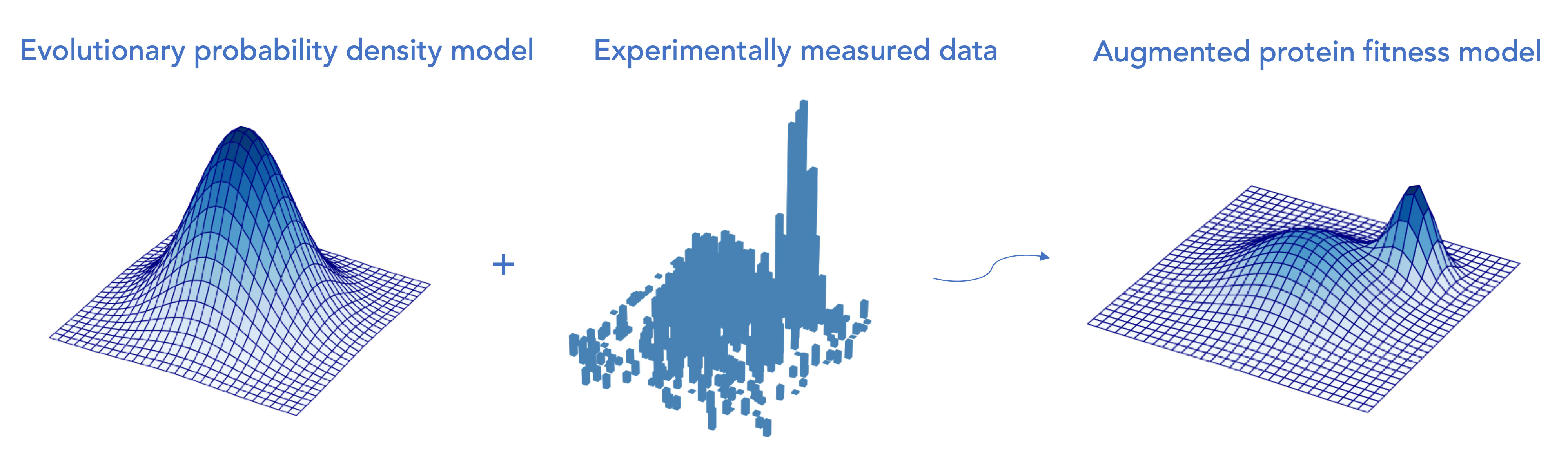
Machine Learning Helps Predict Protein Functions
Computers learn from a combination of experimental and evolutionary data to enhance the function of useful proteins.

Computers learn from a combination of experimental and evolutionary data to enhance the function of useful proteins.

A new model predicts small-scale differences in methane emissions from tropical soils on a hillside during drought and recovery.
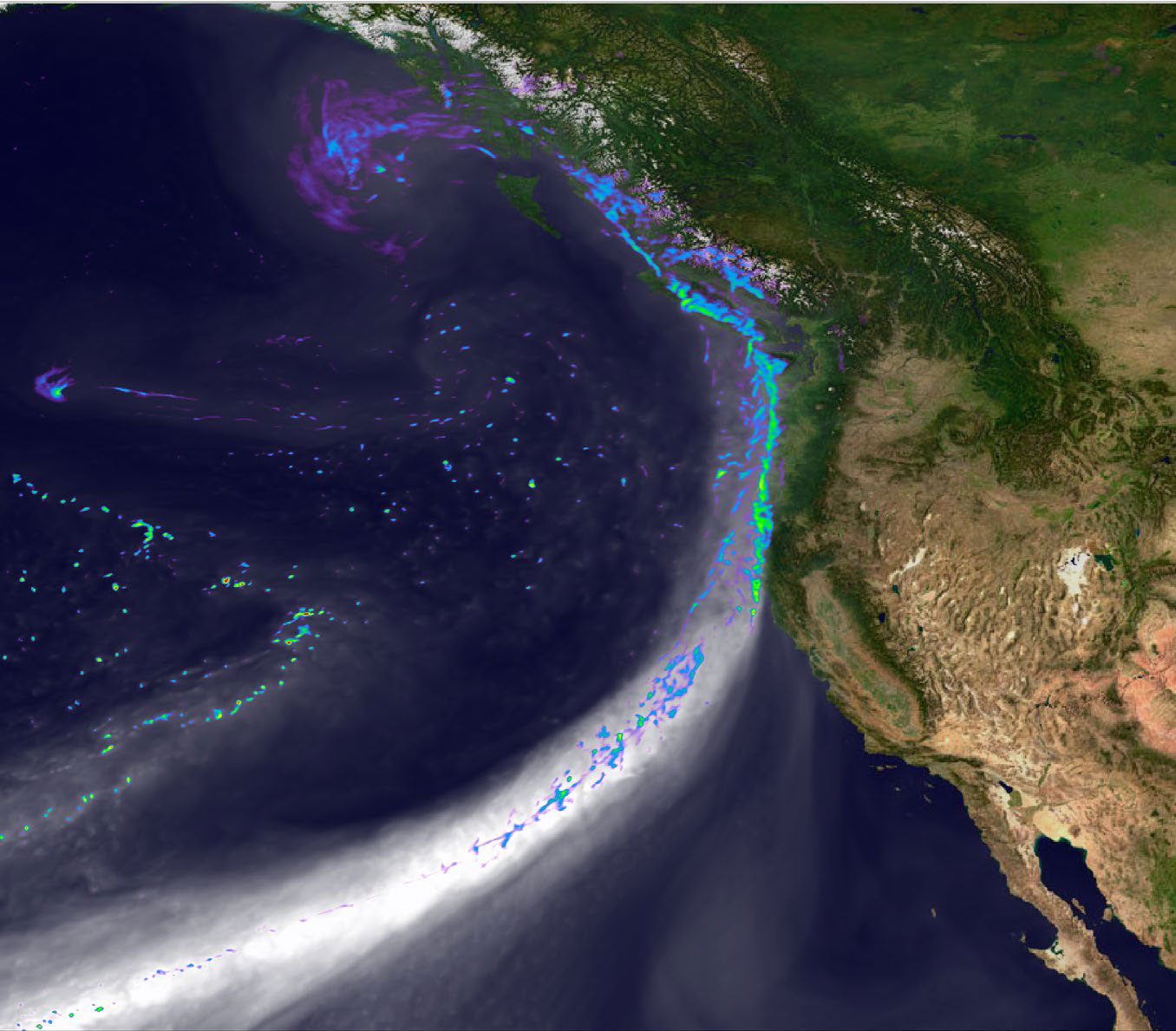
Scientists demonstrate the value of a new global atmosphere model for the Energy Exascale Earth System Model.

Six years of radar data from the Atmospheric Radiation Measurement (ARM) user facility site in Utqiaġvik, Alaska provide important details on how secondary ice particles form in Arctic clouds.
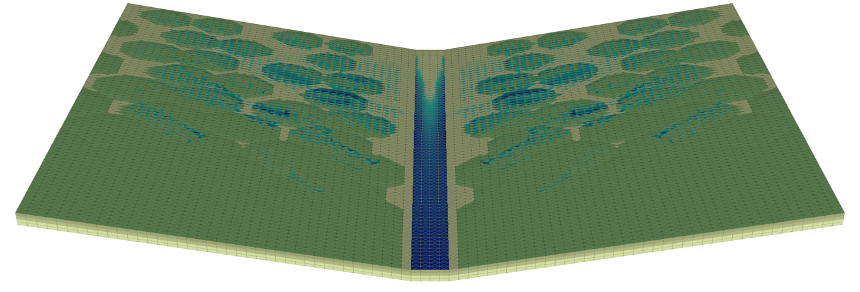
A novel mathematical formulation accurately solves water flow in geometrically complicated soil structures, including overturned soil layers and other disturbances.
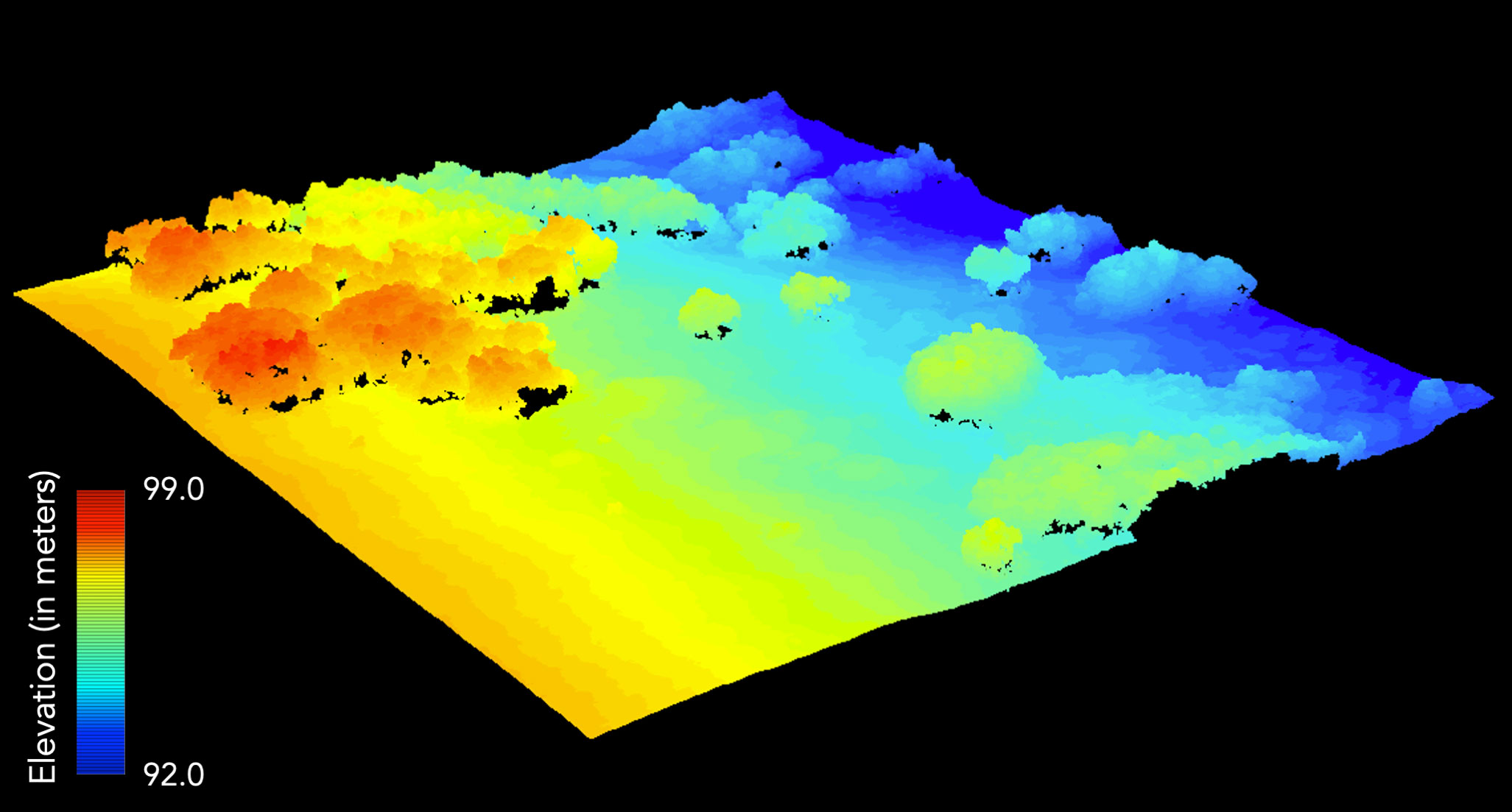
Novel multi-sensor drone imagery enhances our understanding of the spatial patterns of Arctic vegetation.

The tropical Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO) rainfall pattern brings change to non-tropical parts of the United States.
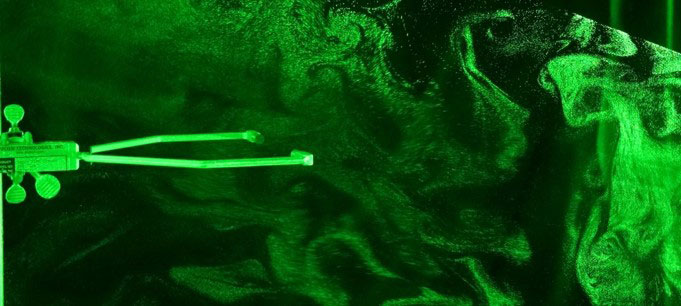
Turbulent air in the atmosphere affects how cloud droplets form. New research changes the way scientists model clouds and, therefore, climate.
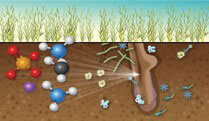
Scientists get a molecular look at how plants and bacteria interact, with insights for agriculture.
Two important factors help determine how much sunlight soot absorbs.

High-yield miscanthus and switchgrass are promising alternatives to traditional annual crops for biofuels.
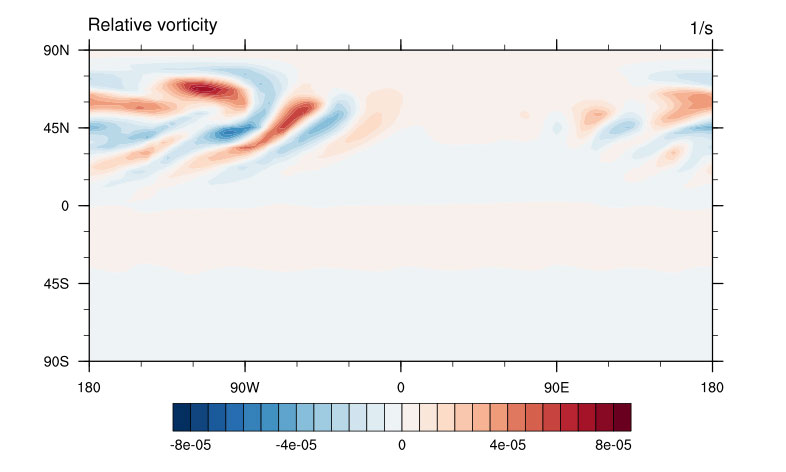
Research produces an improved dynamical core to model the evolution of winds, temperatures, and pressures in the atmosphere.