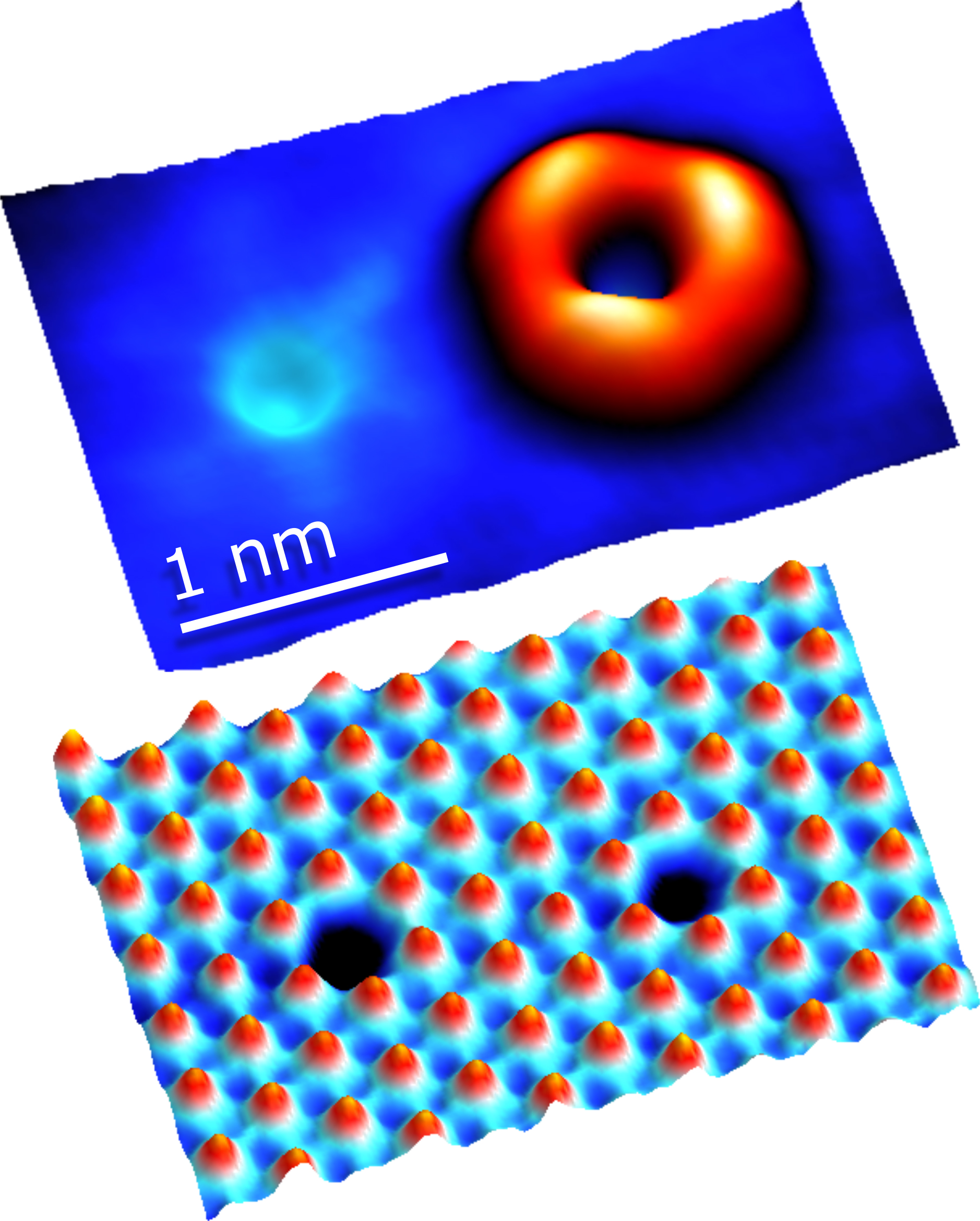
Linking Properties to Defects in 2D Materials
Scientists reveal oxygen’s hidden talent for filling atomic gaps in 2D semiconductors and the surprising role of electron spin in electronic conductivity

Scientists reveal oxygen’s hidden talent for filling atomic gaps in 2D semiconductors and the surprising role of electron spin in electronic conductivity
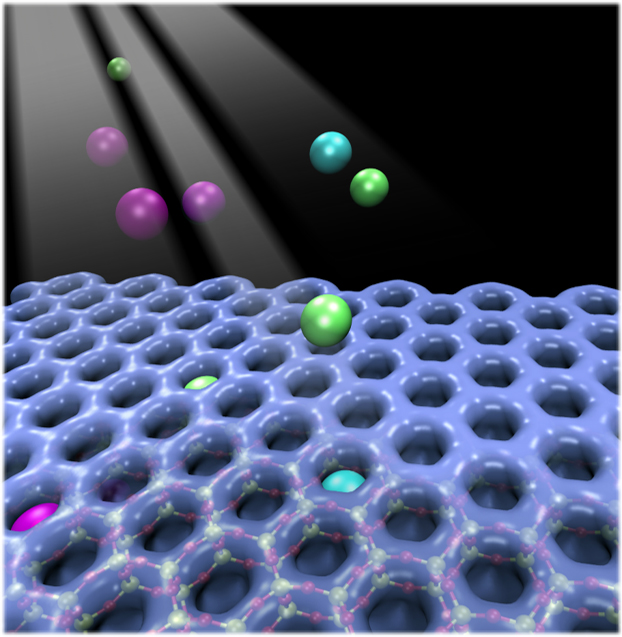
Material traps noble gases at above-freezing temperatures, a difficult and important industrial challenge.
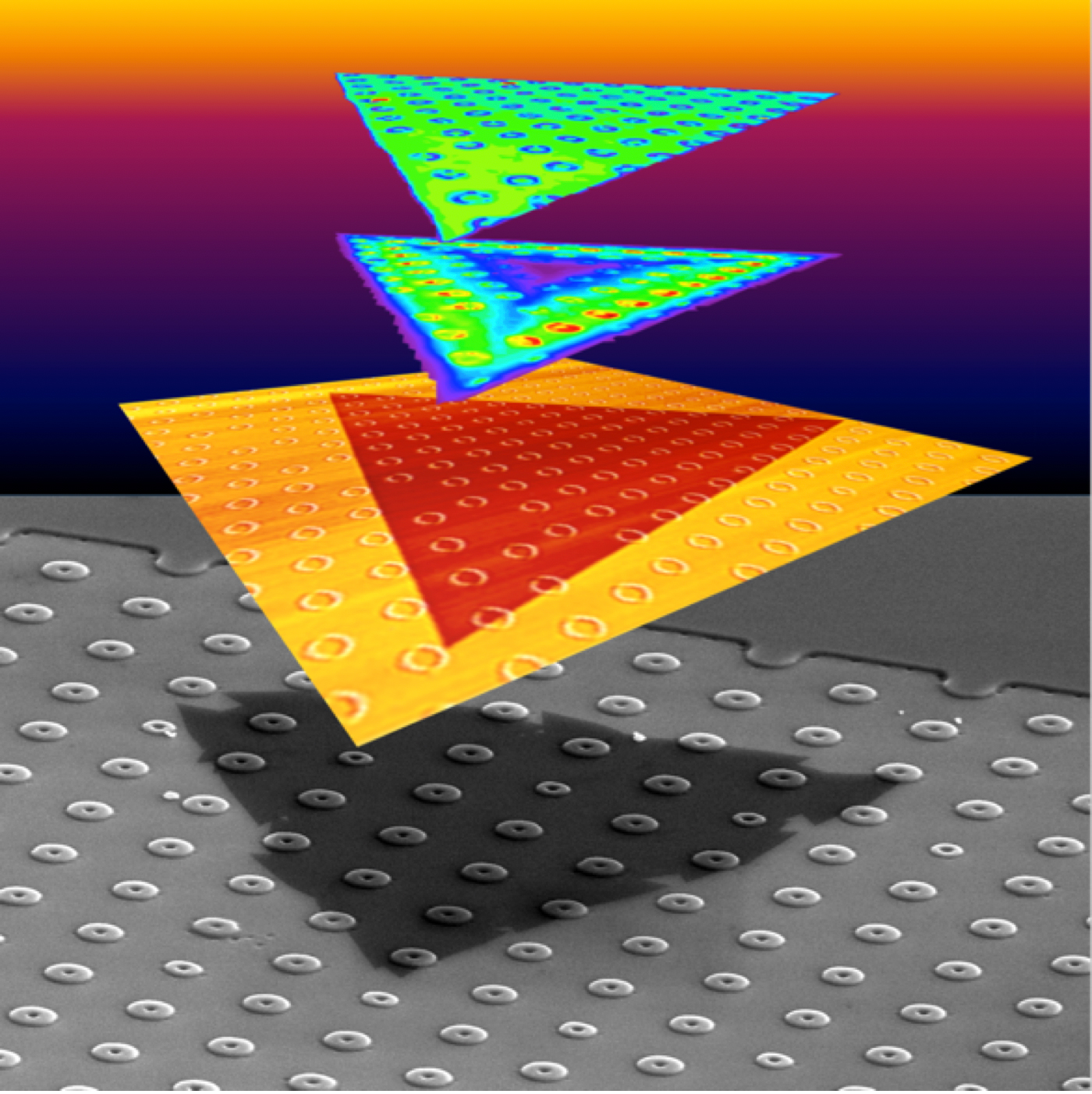
Growing two-dimensional crystals on curved surfaces introduces strain to control the crystal’s light emission.
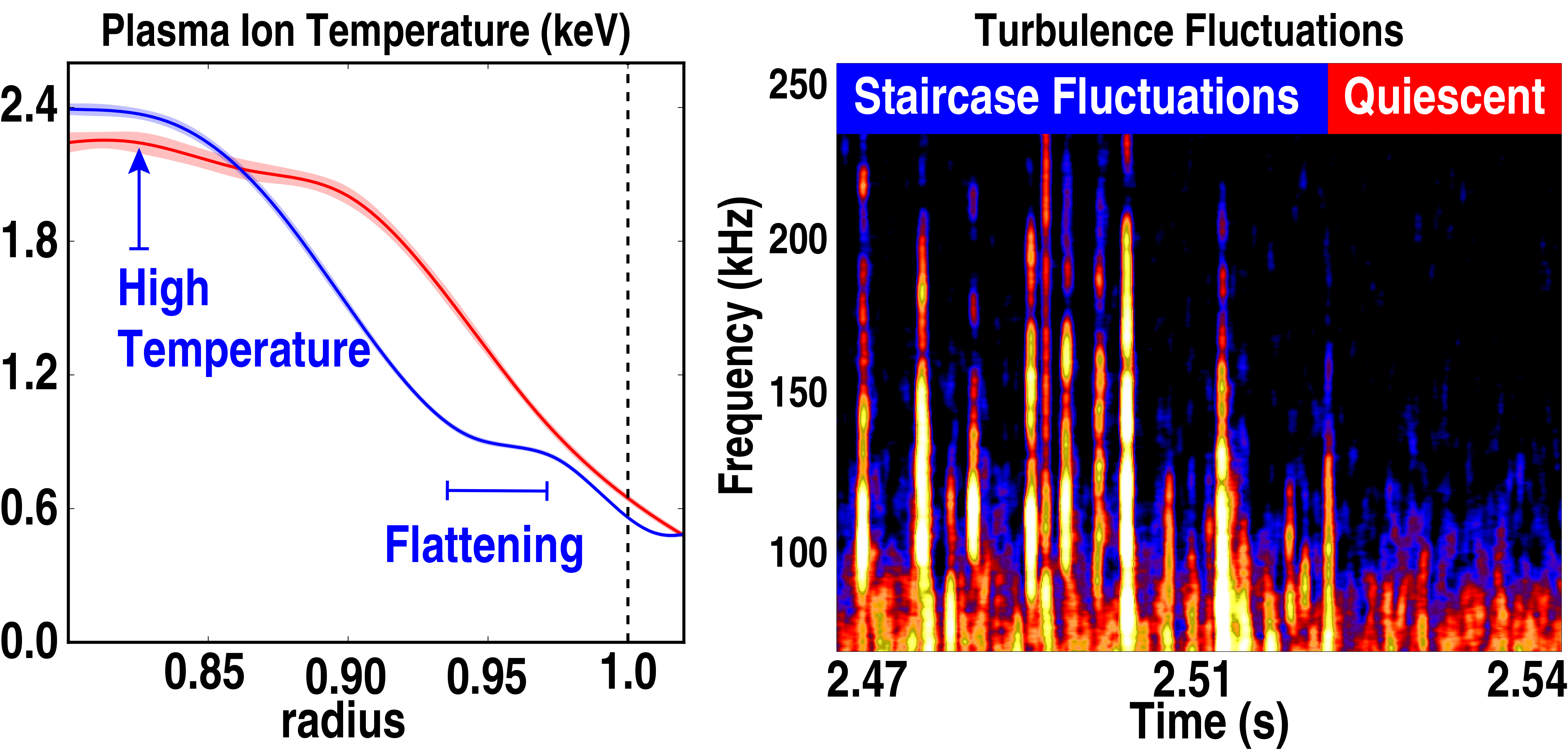
Forming a staircase in the edge of the plasmas can boost the performance of a fusion reactor
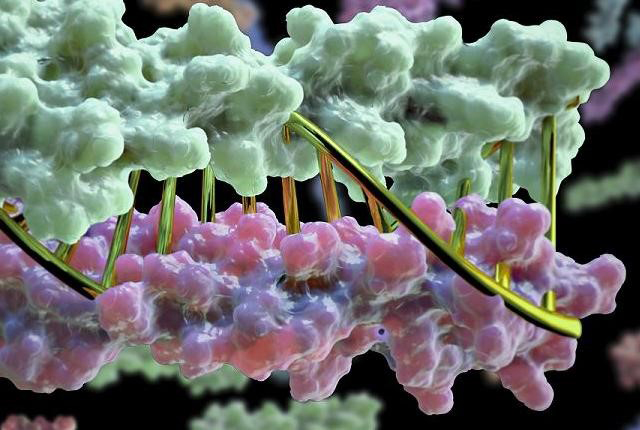
Using advanced computing, scientists designed protein pairs that perfectly complement each other
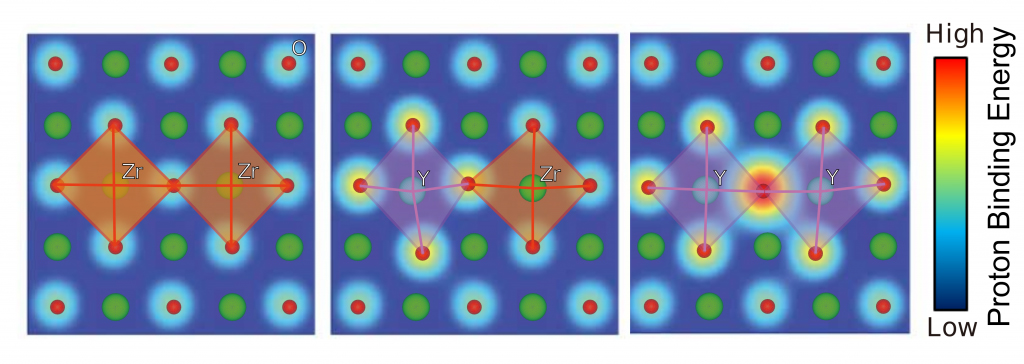
Researchers determine how to design better materials for energy storage.
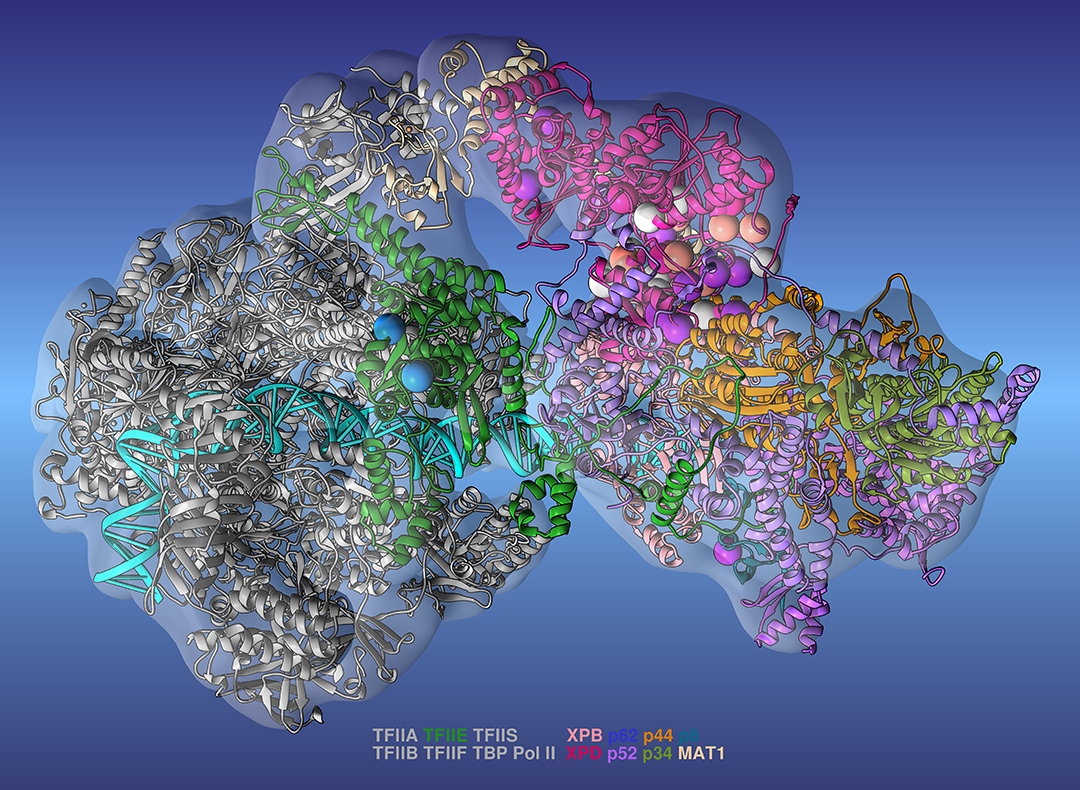
Researchers create the most complete model yet of complex protein machinery.
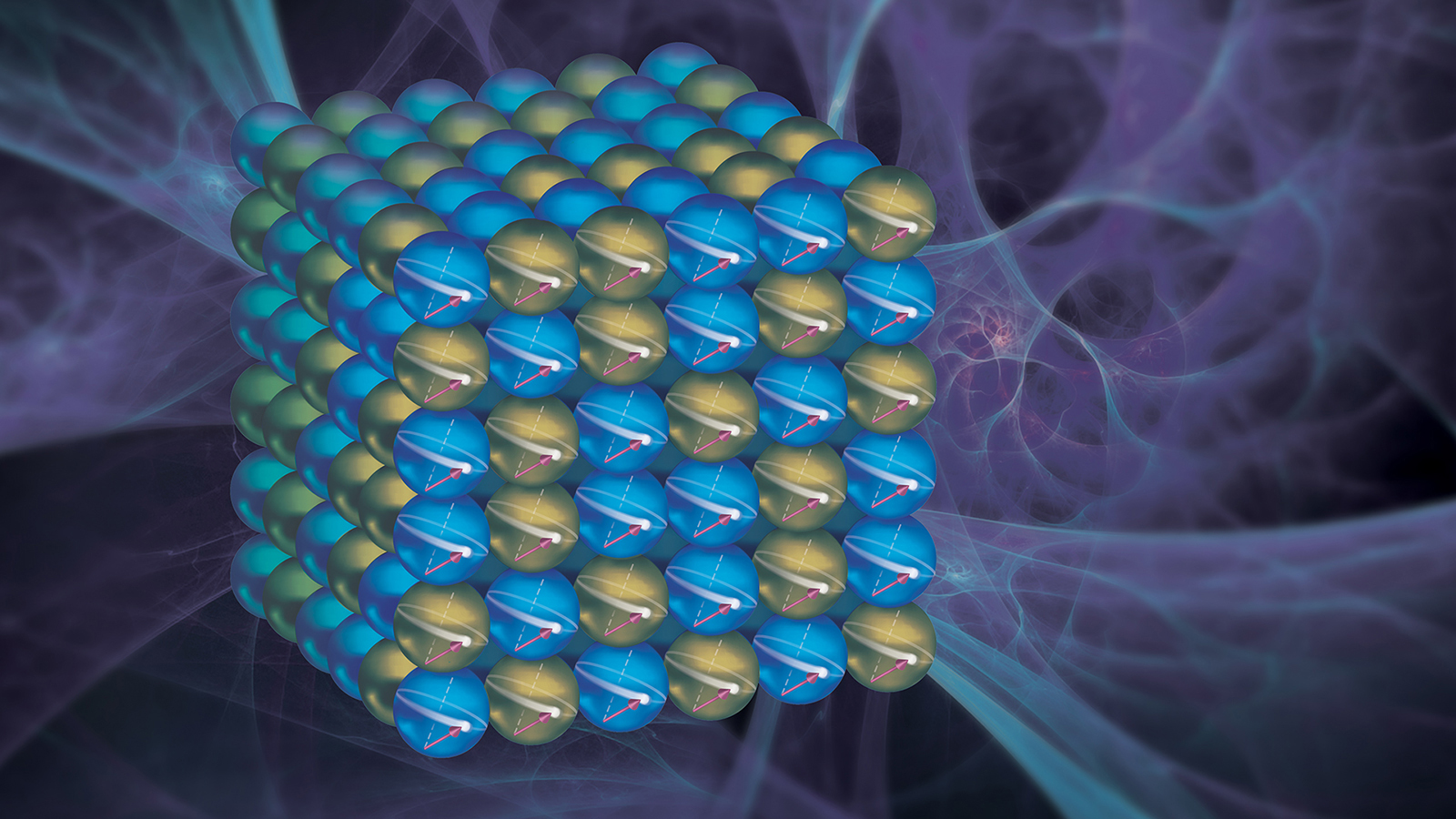
By rotating materials commonly used in computer storage devices, scientists found a new way to change their intrinsic properties
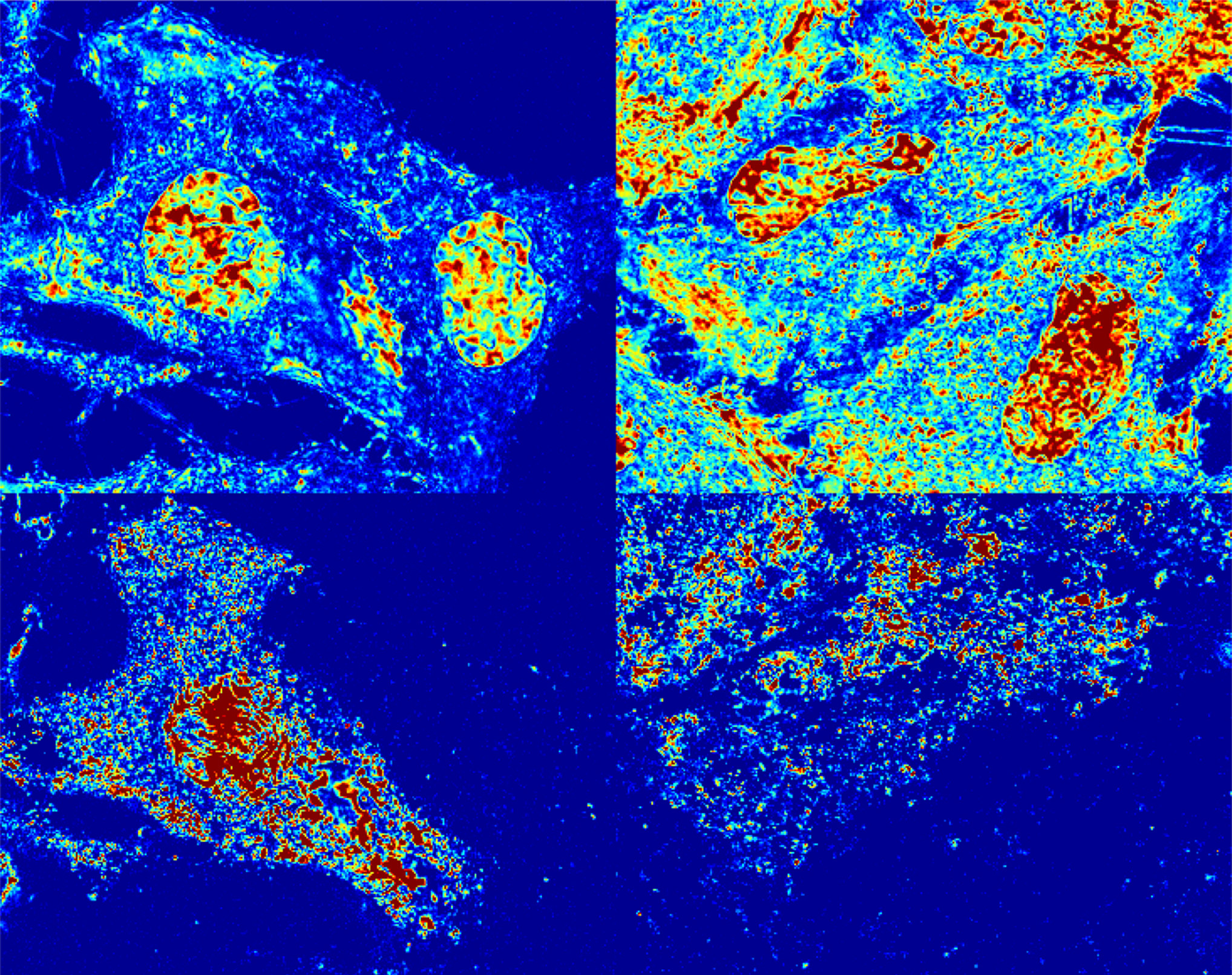
Algorithms supporting a “microscope in a computer” tool enable early screening of several major cancers
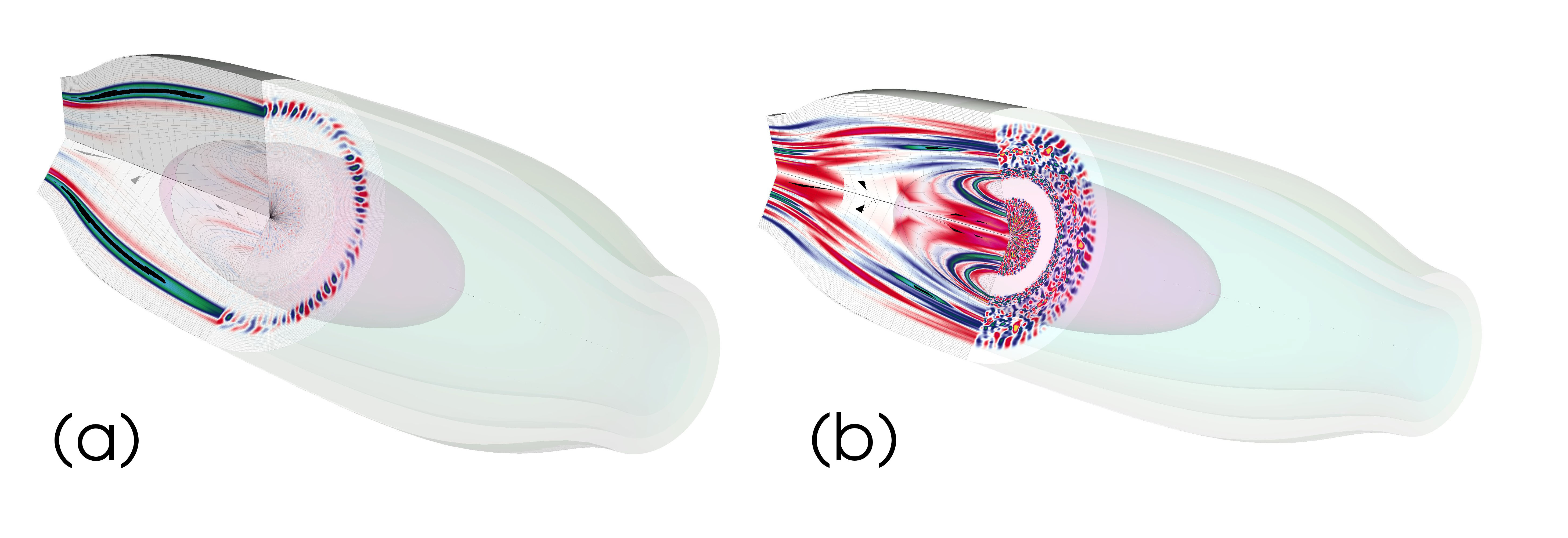
Developing computer models of the plasma in a unique device is helping a company take the next steps towards producing power
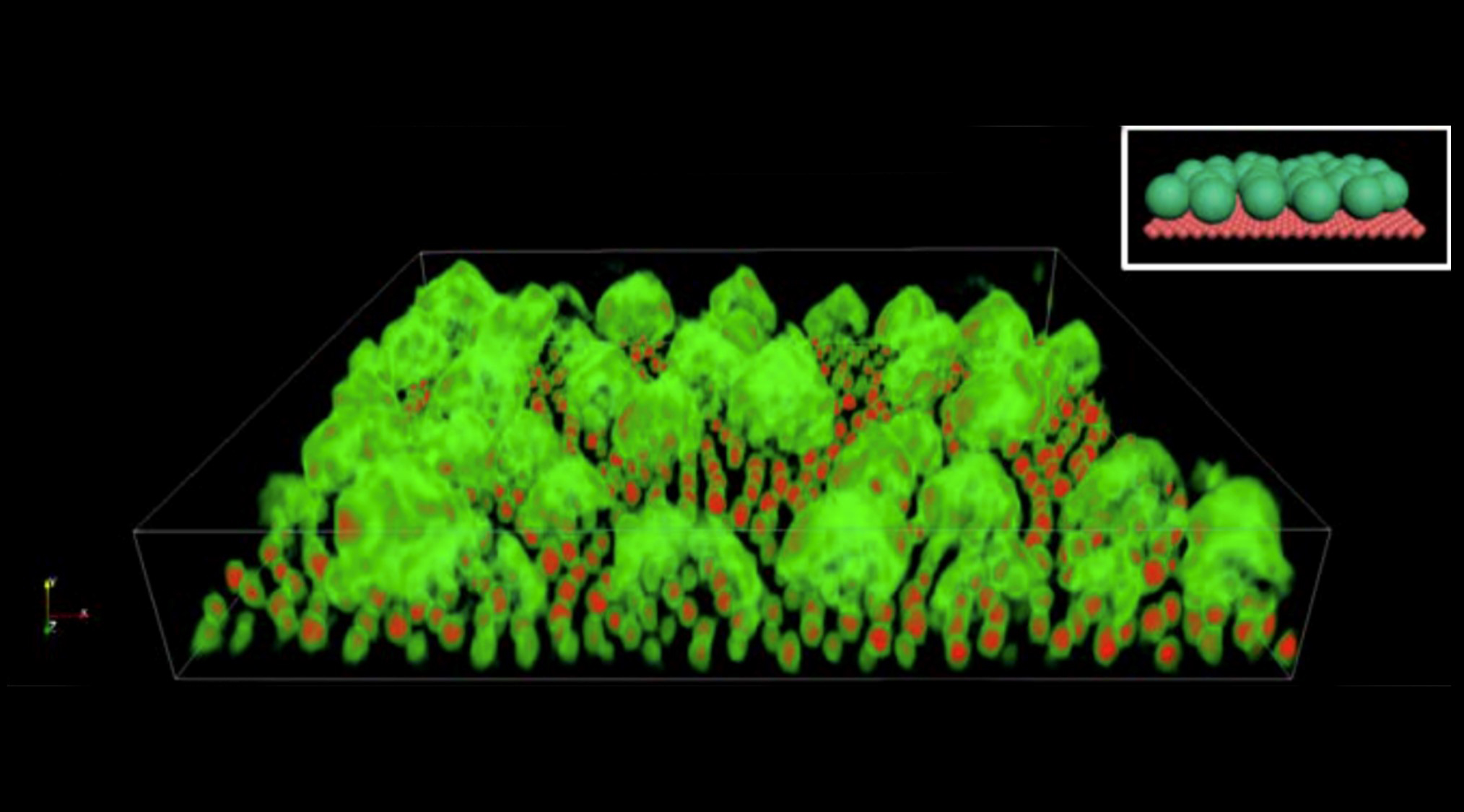
Researchers develop design rules that guide the self-assembly of crystals and frameworks into thin sheets for energy storage and other uses
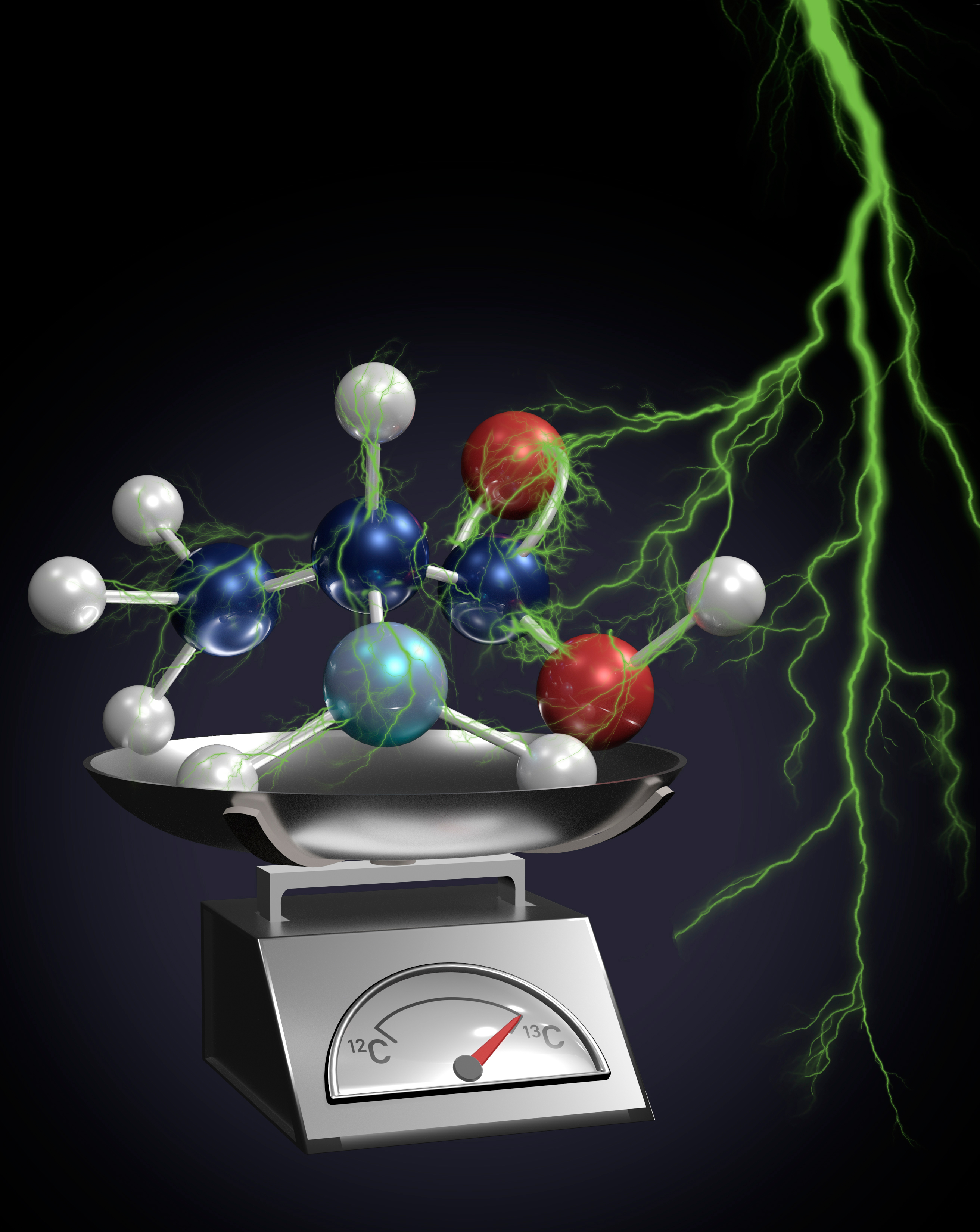
Novel isotope tracking brings nanoscale chemistry into view