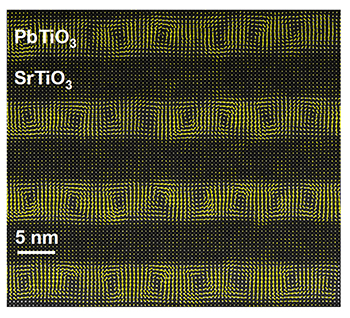
Electronic “Cyclones” at the Nanoscale
New state of matter holds promise for ultracompact data storage and processing.

New state of matter holds promise for ultracompact data storage and processing.
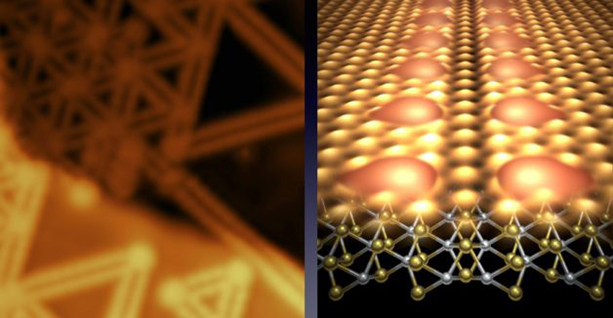
Scientists found that removing lines of atoms in thin electronic materials creates “veins” that could benefit solar panels and more.
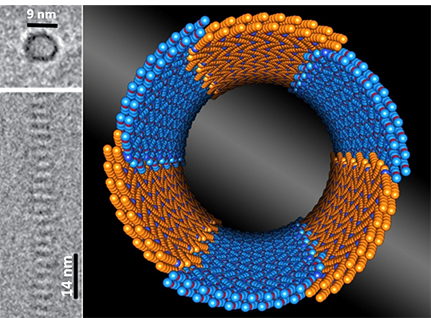
Scientists reveal another design principle for building nanostructures in soft matter, valuable for batteries, water purification, and more.
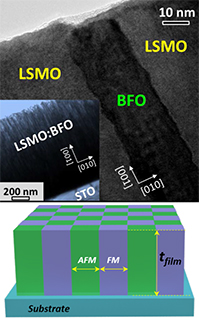
Unique magnetic coupling found in vertically aligned nanocomposite films shrink devices and let them withstand higher temperatures.
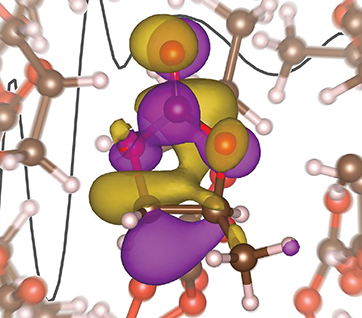
Scientists seek to improve the battery by investigating the detailed interactions lithium ions experience with liquid battery electrolytes.

Researchers reveal the factors that affect the stability of semiconductors in solar fuel devices to aid the discovery of next-generation materials.

Confining water in tiny straws confirms predicted rapid transport of protons along a water “wire”—vital for more efficient fuel cells.
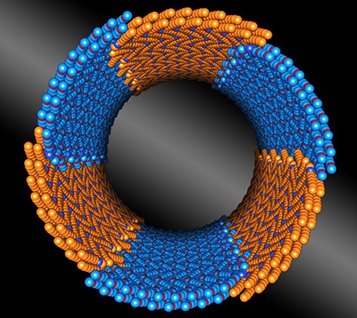
Scientists discover another design principle for building nanostructures.
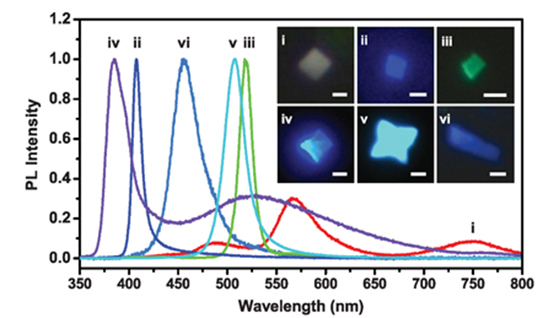
First atomically thin, halide perovskite sheets could be an alternative to graphene for future electronics.
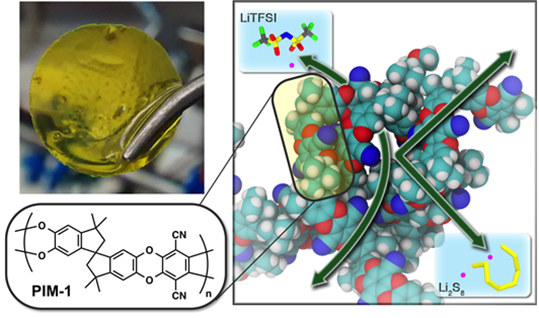
Microporous polymer separator prevents specific molecules from crossing battery and causing degradation and shorter lifetimes.
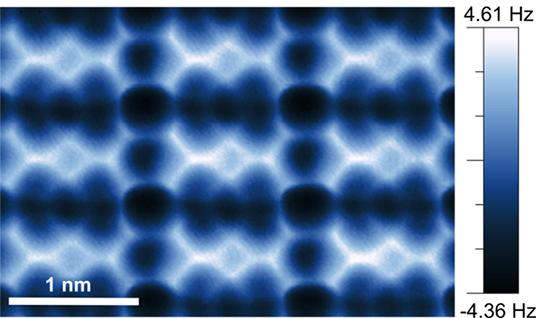
Novel self-assembly can tune the electronic properties of graphene, possibly opening doors for tiny, powerful electronic devices.
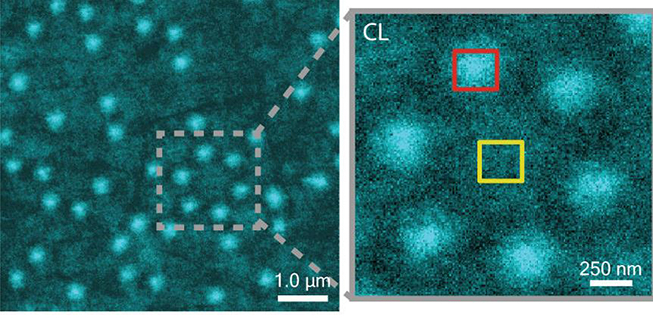
Researchers develop breakthrough technique for non-invasive electron microscopy for soft materials