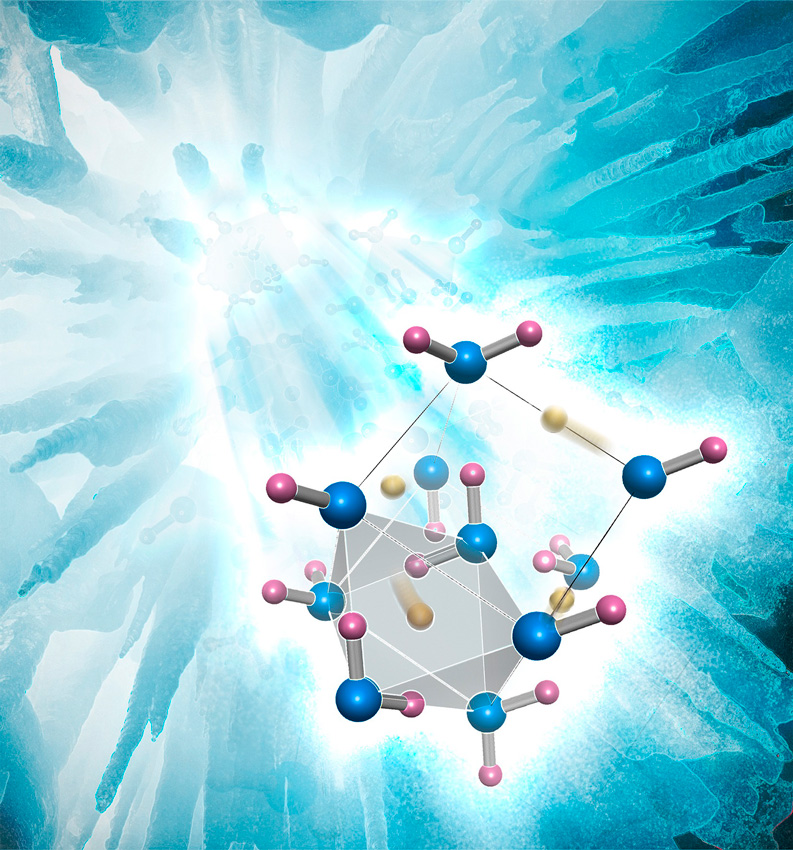

Inside Ice Under High Pressure
New insights from neutron diffraction reveal changes to atomic structure.

New insights from neutron diffraction reveal changes to atomic structure.
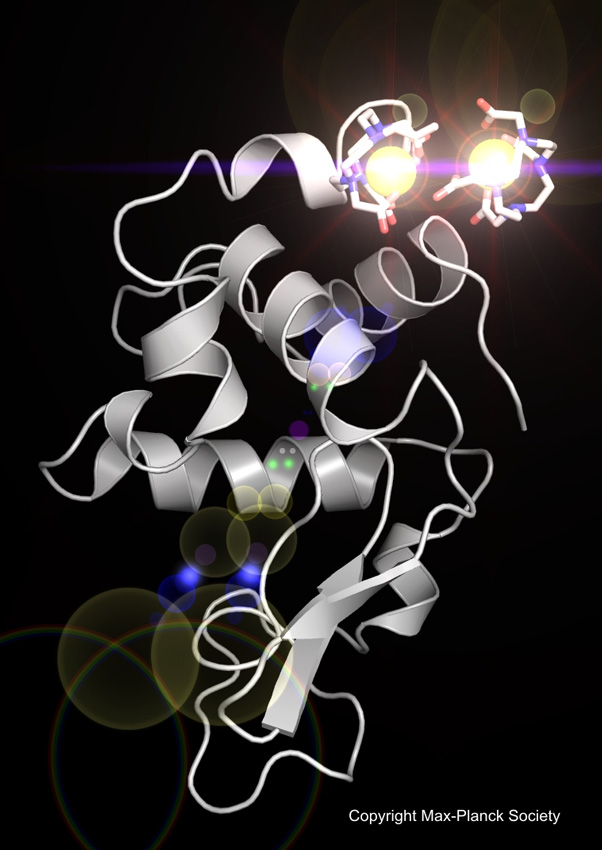
A novel tool to determine the structure of difficult to crystallize proteins.
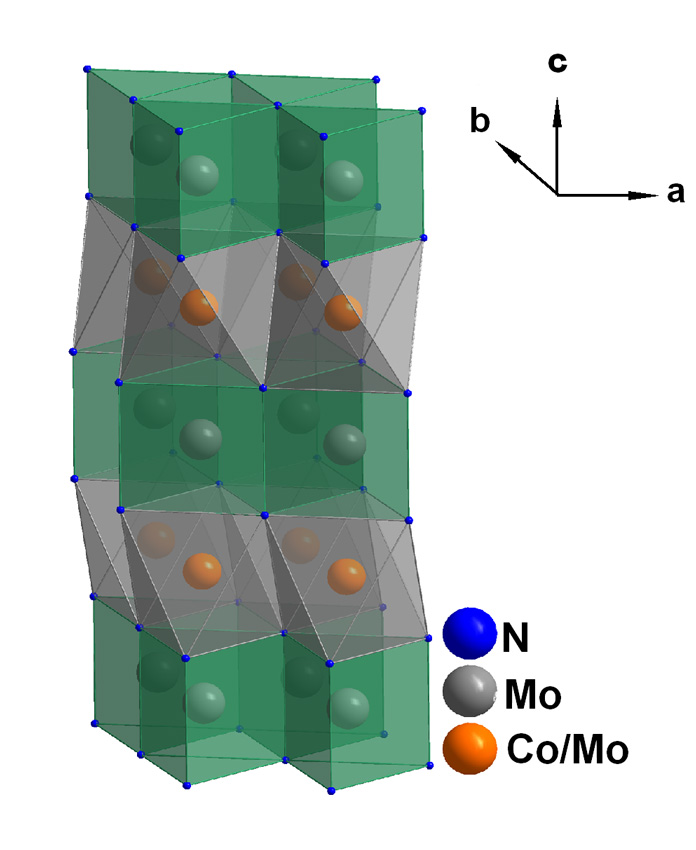
New catalyst material provides potential for cheaper renewable hydrogen production.
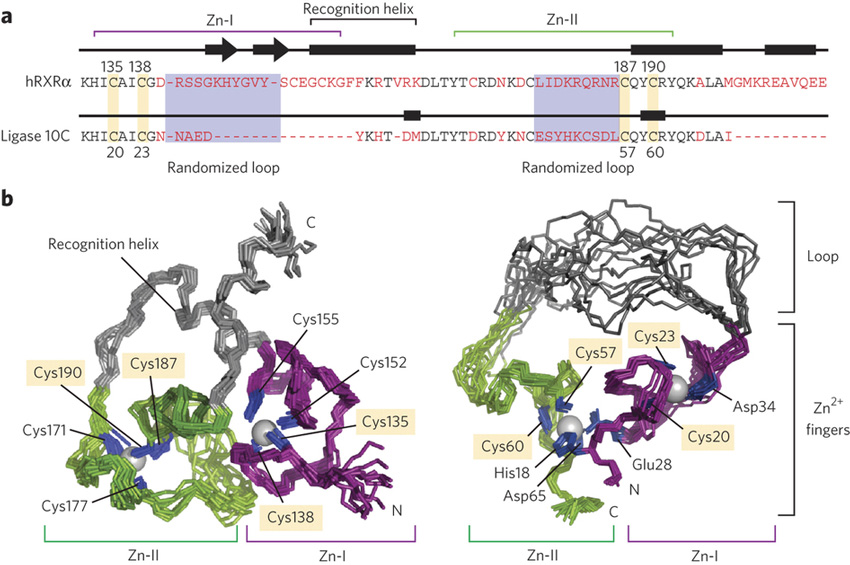
Study reveals structural changes leading to catalytic activity.
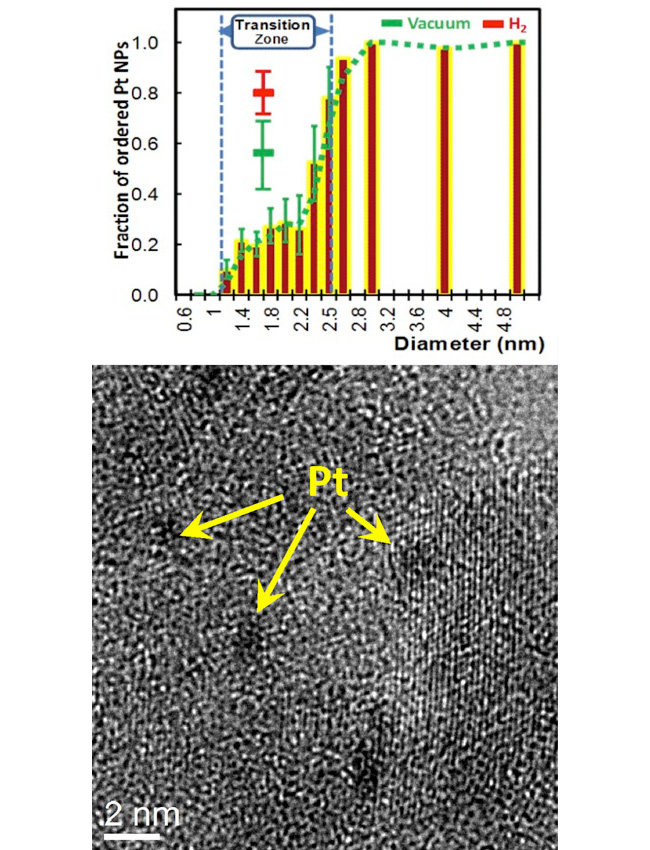
Discovery of coexisting ordered and disordered catalytic nanoparticles.
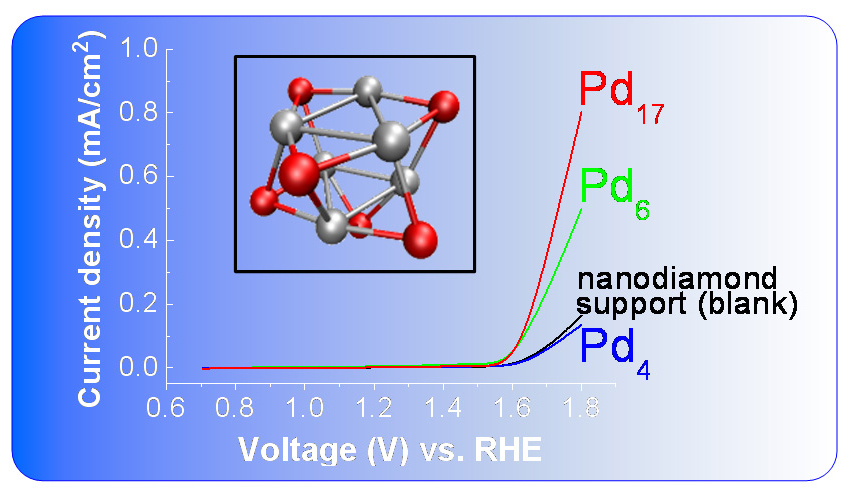
Groups of Palladium atoms found to have major effects on electrocatalyst performance.
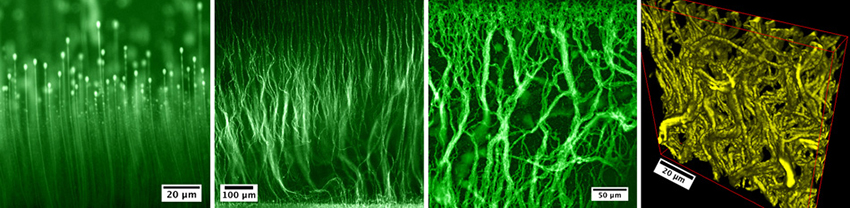
Electric fields control growth of “sticky” polymer particles.
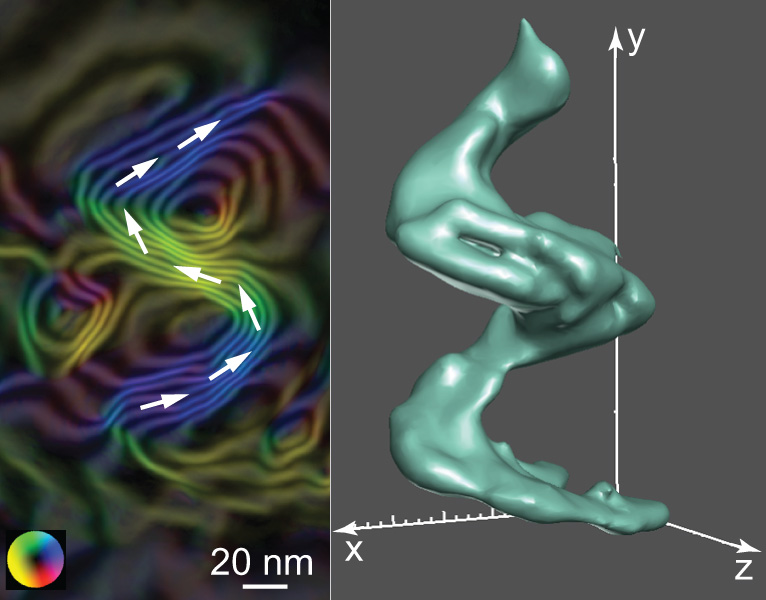
Direct visualization of magnetic structures gives researchers a window into new possibilities at the Nanoscale.
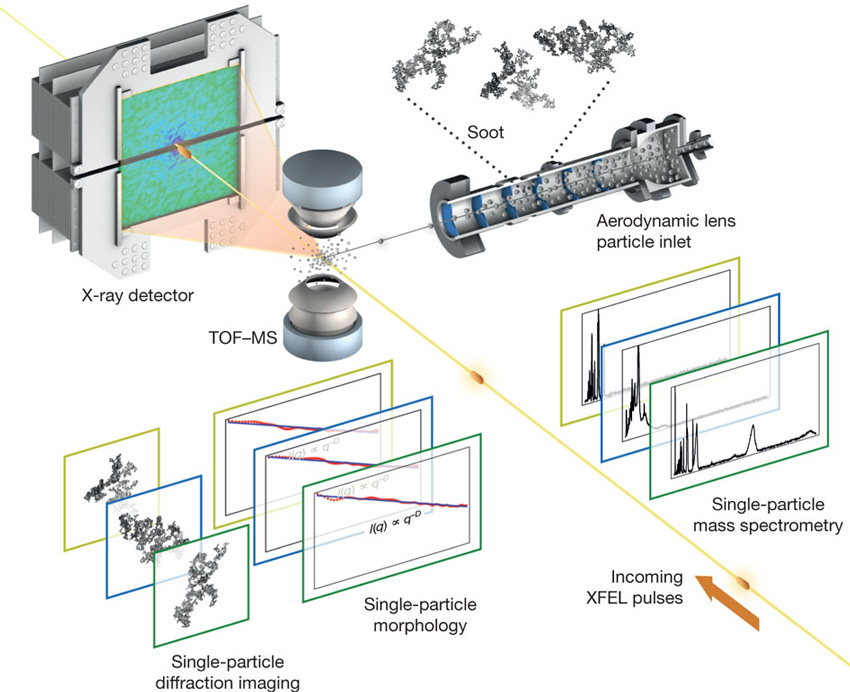
Soot particle diversity and complexity discovered using ultrafast x-rays at the Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS).
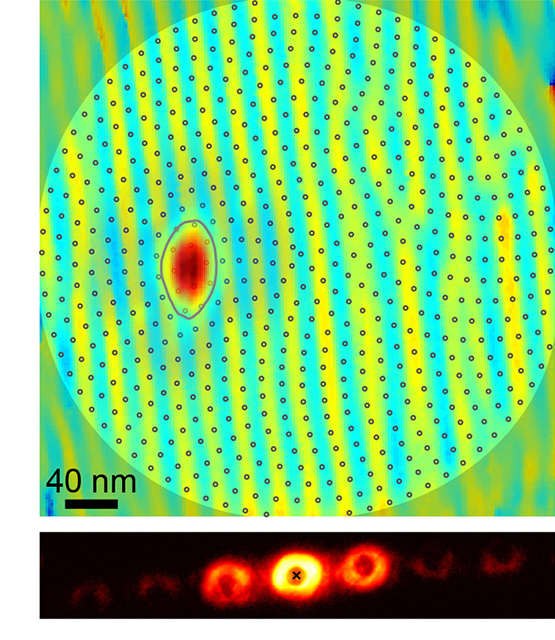
Researchers have invented a new x-ray imaging technique that could reveal key atomic-scale properties in ferroelectric magnetic materials.
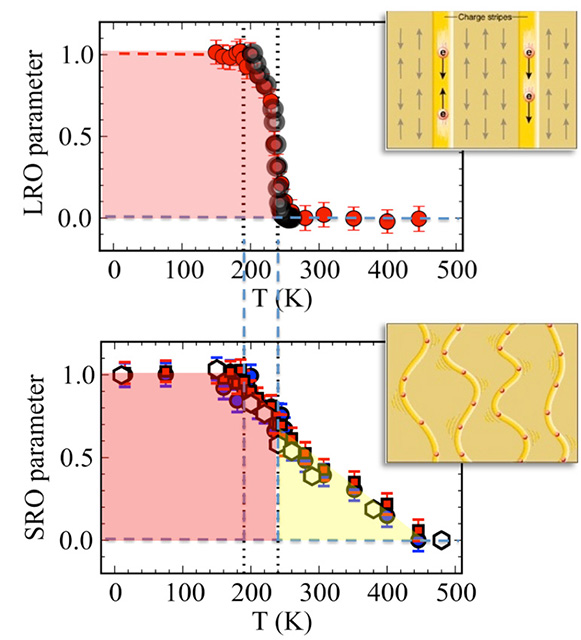
Using neutron diffraction, movement of charged atoms arranged as “stripes” was captured for the first time.
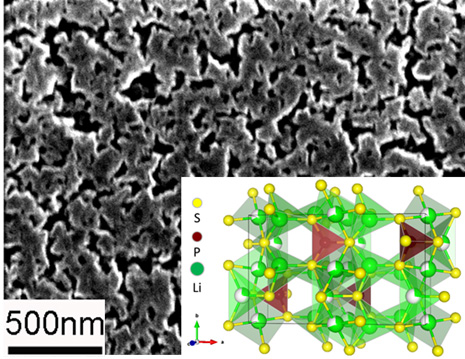
Using sulfur-rich, highly ionic compounds as cathodes and electrolytes enables solid-state lithium-sulfur rechargeable batteries.